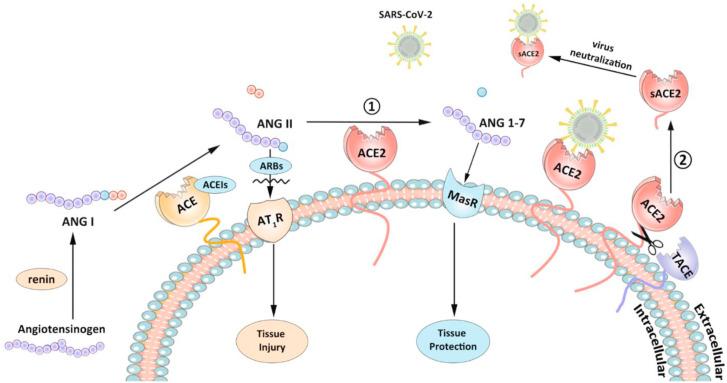
Fig. 1.
Two pathways related to beneficial activity of ACE2 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Angiotensin I (ANG I) generated from angiotensinogen by renin, can subsequently be catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and produce angiotensin II (ANG II). On the one hand, ANG II binds to angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT1R) to cause tissue injury. On the other hand, ACE2 can convert ANG II to angiotensin 1-7 (ANG 1–7), which can protect against tissue damage through Mas receptor (MasR). Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) can suppress the destructive function of Ang II. ACE2 is also the receptor of SARS-CoV-2. And ACE2 can meanwhile be cleaved by TNF-α converting enzyme (TACE) into soluble forms, namely sACE2, which will be released into extracellular compartments and neutralize SARS-CoV-2.