Fig. 4.
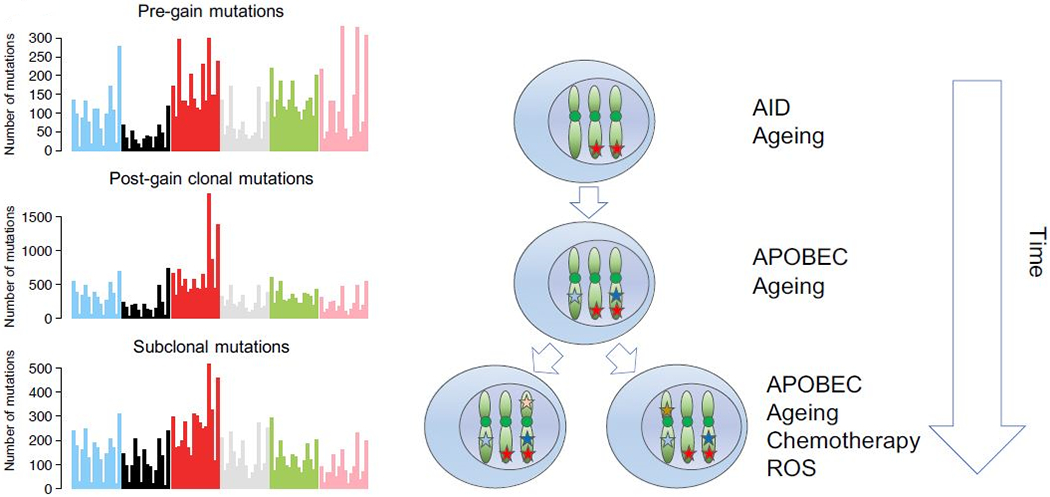
Illustration of how to reconstruct the mutational signature activity over time in multiple myeloma. When an allele is duplicated, all the mutations acquired since the fertilized egg will be duplicated and present on the two duplicated alleles. This will change their VAF from 50% to 66%. In contrast, all the mutations acquired after the duplication will be present only on one allele and have a 33% VAF. Differentiating pre and post gain mutations allows to explore the chronological order of clonal events. Combining this with data from phylogenic tree reconstruction (i.e. clonal vs subclonal) we can divide a faction of genomic events in early (pre gain), intermediate (post gain) and late (subclonal). Doing so on 52 WGS, we observed different patterns of mutations and signatures. Specifically, AID tends to dramatically decrease from pre to post gain (e.g. T>G peaks); APOBEC increase after gains (e.g. peaks in A[C>T]T and T[C>T]T); chemotherapy signatures are acquired later G[C>G]X, in line with their post-diagnosis acquisition.
