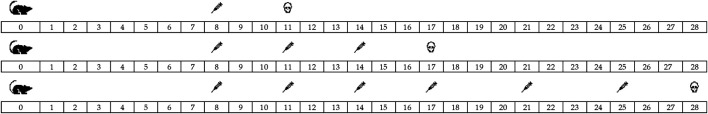
FIGURE 1.
Experimental design for thioredoxin treatment of control and rd1 mice (TRX dose: 5 mg/kg weight; via: i.p.). Numbers indicate postnatal day. Group 1: control mice that received vehicle treatment at P8 and were euthanized at PN11; Group 2: control mice that received TRX treatment at P8 and were euthanized at PN11; Group 3: rd1 mice that received vehicle treatment at P8 and were euthanized at PN11; Group 4: rd1 mice that received TRX treatment at P8 and were euthanized at PN11; Group 5: control mice treated with vehicle at PN8, PN11, and PN14 and euthanized at PN17; Group 6: control mice treated with TRX at PN8, PN11, and PN14 and euthanized at PN17; Group 7: rd1 mice treated with vehicle at PN8, PN11, and PN14 and euthanized at PN17; Group 8: rd1 mice treated with TRX at PN8, PN11, and PN14 and euthanized at PN17; Group 9: control mice that received vehicle treatment at PN8, PN11, PN14, PN17, PN21, PN25 and were euthanized at PN28; Group 10: control mice that received TRX treatment at PN8, PN11, PN14, PN17, PN21, PN25 and were euthanized at PN28; Group 11: rd1 mice that received vehicle treatment at PN8, PN11, PN14, PN17, PN21, PN25 and were euthanized at PN28; Group 12: rd1 mice that received TRX treatment at PN8, PN11, PN14, PN17, PN21, PN25 and were euthanized at PN28.