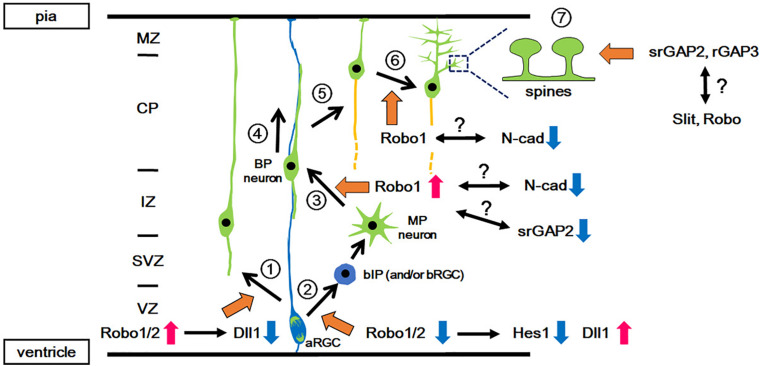
FIGURE 1.
Functions of Slit-Robo signaling in various events during neocortical development. During development, pyramidal projection neurons are directly generated from the aRGCs in the VZ (1: Direct neurogenesis) or via intermediate progenitors (2: Indirect neurogenesis). In indirect neurogenesis, bIPs give rise to neurons with multipolar processes (MP neurons) and then the MP neurons transform into bipolar (BP) neurons (3: MP-BP transition). The BP neurons migrate along the basal processes of the aRGCs toward the CP (4: Locomotion). When the BP neurons reach the upper part of the CP, they detach from the basal processes and migrate a short distance to the pial surface (5: Terminal translocation). Then, the neurons develop dendrites (6: Dendrite formation) followed by spine formation on the dendrites (7: Spine formation). Orange arrows indicate the involvement of Slit-Robo signaling and/or srGAP. Red and blue arrows indicate the activation and inactivation of molecules/signals, respectively. aRGC, apical radial glial cell; bIP, basal intermediate progenitor; BP, bipolar; CP, cortical plate; IZ, intermediate zone; MP, multipolar; MZ, marginal zone; N-cad, N-cadherin; SVZ, subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone.