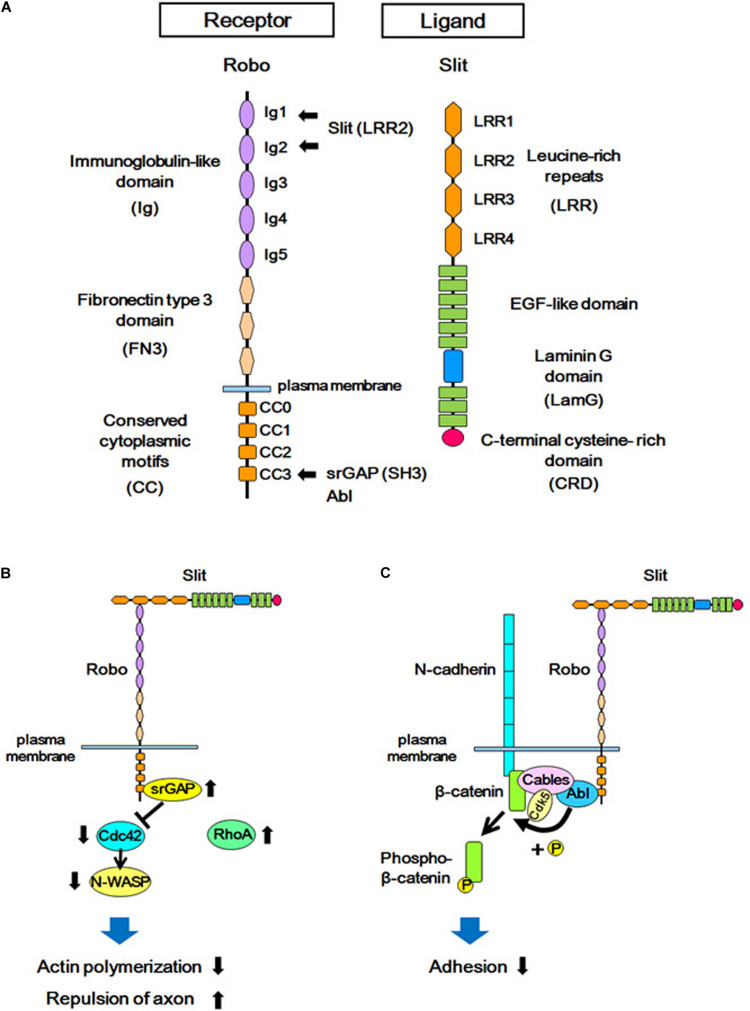
FIGURE 2.
Structures of Slit/Robo, and the Slit-Robo signaling pathway. (A) The Robo receptor contains five immunoglobulin-like domains (Ig), three fibronectin type III domains (FN3), and four conserved cytoplasmic domains (CC). Slit is a secreted glycoprotein and a major ligand of the Robo receptor. Slit contains four domains consisting of leucine-rich repeats (LRR), several EGF-like sequences, a laminin-G domain (LamG), and a C-terminal cysteine-rich domain (CRD). The LRR2 domain of Slit interacts with the Ig1 and Ig2 domains of Robo, and the SH3 domain of srGAPs and Abl kinase interacts with the CC3 domain of Robo. (B) The extracellular interaction between Slit and Robo increases the binding of srGAP with Robo, resulting in the activation of srGAP. Activated srGAP induces GTP hydrolysis of Cdc42, and therefore inactivates Cdc42. Inactivated Cdc42 is unable to stimulate actin polymerization via the downstream effector of Cdc42 (N-WASP). This in turn leads to actin depolymerization and repulsion of the axon. (C) Binding of Slit to Robo results in the interaction between Abelson (Abl) and Cable, which leads to tyrosine phosphorylation of β-catenin by Abl. This phosphorylation reduces the affinity between β-catenin and N-cadherin, and attenuates N-cadherin-mediated adhesion.