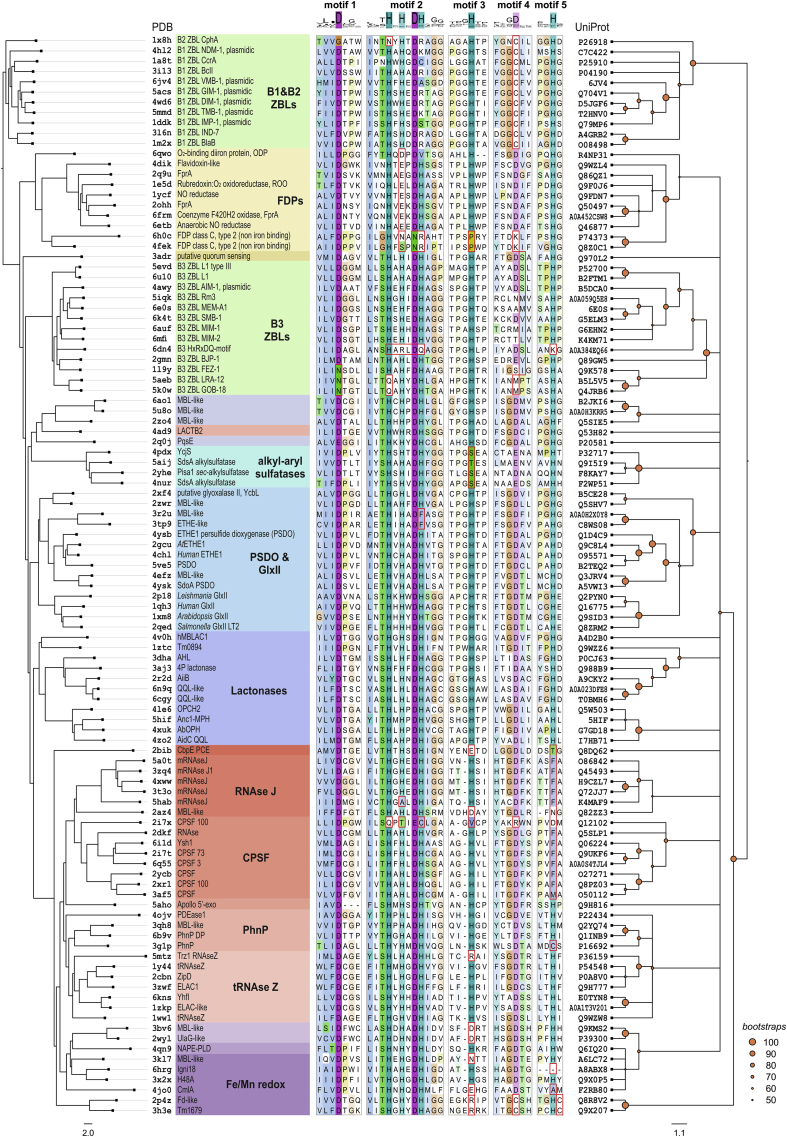
Figure 2.
Structure-function tanglegram of the MBL superfamily. Structure-guided phenogram (left) and the maximum-likelihood MSA-based bootstrapped consensus cladogram (right) of 105 selected MBLs available in the Protein Data Bank. Note that the MSA includes only conserved amino acid residues in the αββα fold, i.e. it does not take into account additional domains. For each dendrogram, taxa are indicated as representative PDB entries (used for structural phenogram calculation) or UniProt entries (used for MSA and cladogram calculation), respectively. A short version of the MSA is provided, comprising the corresponding sequences sorted with the tanglegram, showing the five MBL fold conserved sequence motifs as histogram logos (top), along with short descriptions of common protein names and families (colored boxes). While motif 1 contains a conserved aspartic acid residue involved in stabilization of the MBL fold near the active site; motifs 2, 3, 4 and 5 usually contain metal-coordinating residues. In general, Fe(II)/Fe(III) binding sites typical of MBL oxidoreductases exhibit more acidic residues than Zn(II) binding sites, often found in MBL hydrolases. Distinctive residues of each protein family or group are indicated in the MSA as red boxes. Amino acid sequence lengths are variable between these motifs, ranging 6–503 residues before motif 1 (N-terminus); 9–77 residues between motifs 1 and 2; 3–23 residues between motifs 2 and 3; 11–65 residues between motifs 3 and 4; 14–241 residues between motifs 4 and 5; and 0–58 residues after motif 5 (C-terminus). Orange dots in consensus cladogram nodes indicate bootstrap branch support values higher than 50 %.