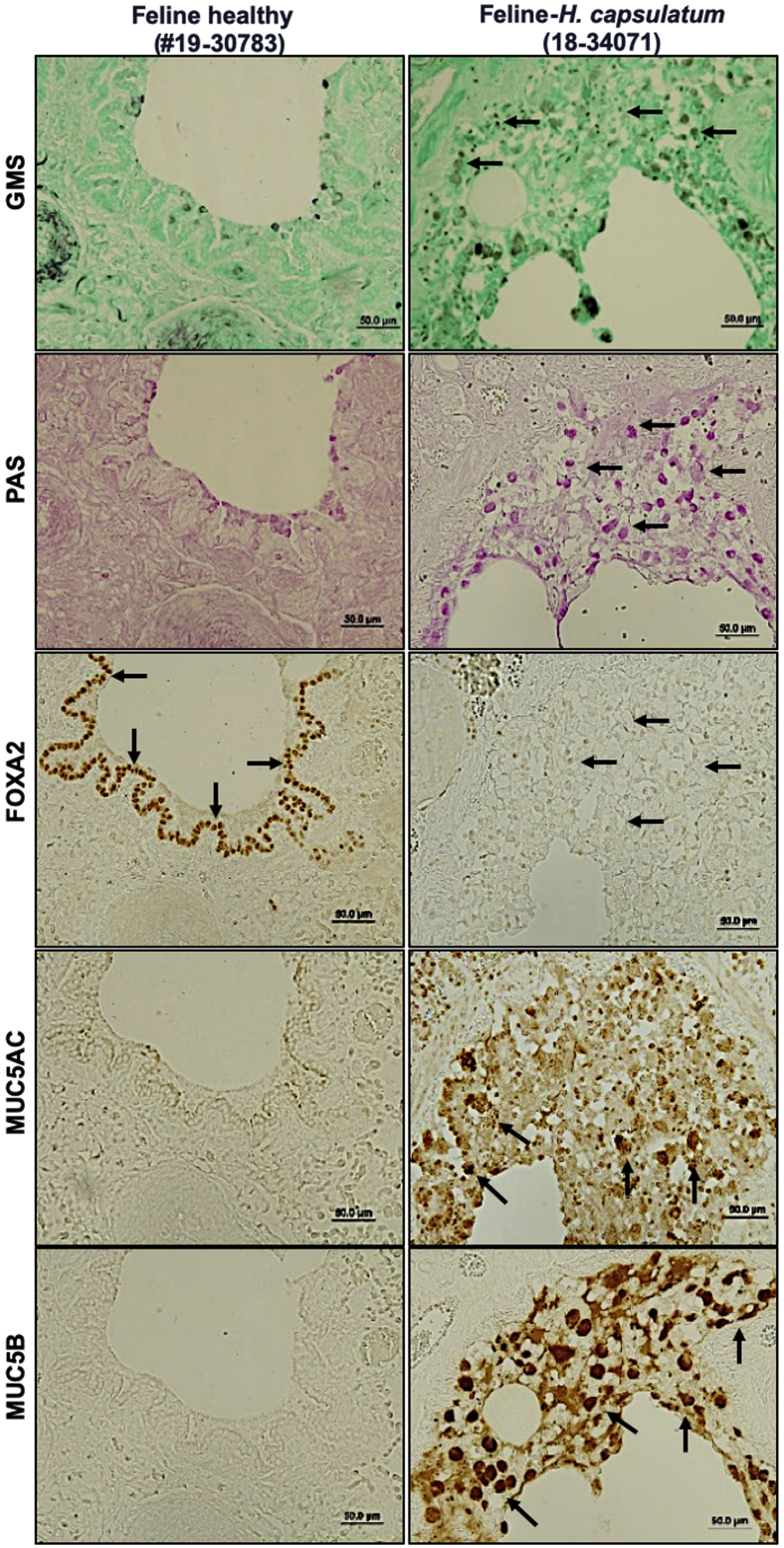
Supplemental Figure S3.
Airway expression of forkhead box protein A2 (FOXA2) is inversely correlated with mucin abundance in feline pulmonary mycosis. Paraffin-embedded lung sections from healthy and fungal-infected animals were stained with Grocott methenamine silver (GMS), periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) for the presence of Histoplasma capsulatum and the expression of FOXA2 and mucins. Healthy control lung sections stained negative for fungal organisms under GMS staining (with yet some visible non-specific background staining), along with basal expression of mucins confirmed by PAS and IHC methods, and strong expression of FOXA2 in bronchial surface epithelia (black arrows). In contrast, fungal-infected feline lungs were positive for yeast bodies under GMS staining (black spots; black arrows) in the bronchial lumens, accompanied by positive PAS staining (pink spots; black arrows) in surface epithelia, which colocalized to the regions expressing MUC5AC and MUC5B in IHC (black arrows). FOXA2 expression was depleted (black arrows). Scale bars = 50 μm.