Figure 10.
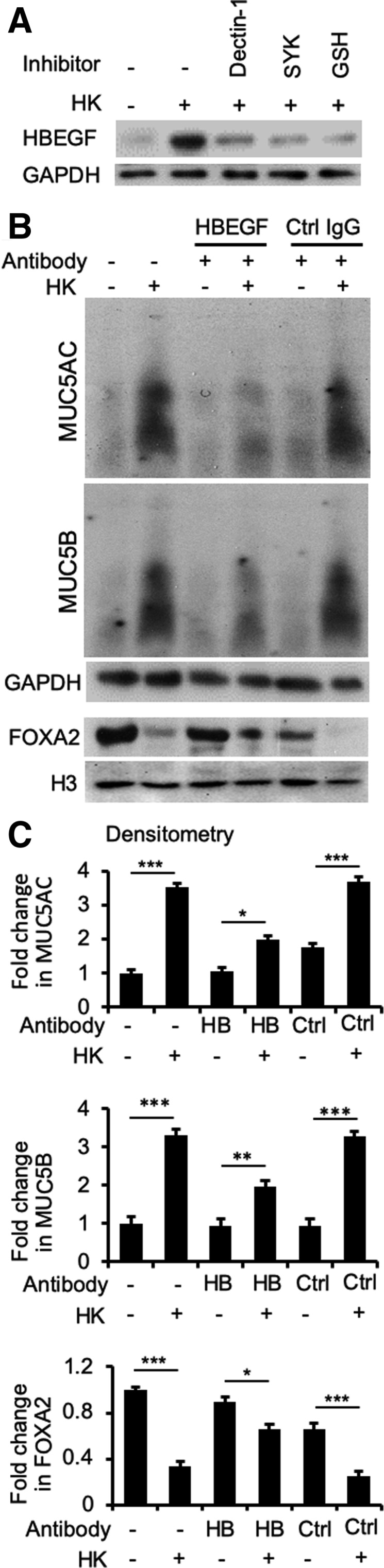
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HBEGF) bridges SYK and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in airway epithelial cells exposed to Blastomyces dermatitidis. A: Immortalized canine airway carcinoma (BACA) cells were pre-exposed to the SYK inhibitor piceatannol (20 μmol/L) or glutathione (5 mmol/L) for 1 hour before challenged with heat-killed (HK) B. dermatitidis strain SCB-2 [multiplicity of infection (MOI) 5:1] for 24 hours. Control cells were exposed to the same volume of sterile phosphate-buffered saline. Membrane, cytoplasmic, and nuclear protein extracts were probed with antibody against each protein. H3 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were used as additional loading controls. B and C: Antibody neutralization of HBEGF restores forkhead box protein A2 (FOXA2) to attenuate mucin expression. BACA cells were pretreated with anti-HBEGF antibody (HB; 1 μg) or an irrelevant control mouse IgG (Ctrl; 1 μg) for 2 hours before 24 hours of exposure to heat-killed B. dermatitidis (MOI 5:1). GAPDH and H3 were used as loading controls. The experiments were independently performed three times with similar results. Western blots from one typical experiment are shown. Additional replicates of Western blots can be found in Supplemental Figure S7. Expression levels of MUC5AC, MUC5B, and FOXA2 were measured by using the ImageJ software version 1.52a. Densitometry data are expressed as means ± SEM from all three experiments (C). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (t-test).
