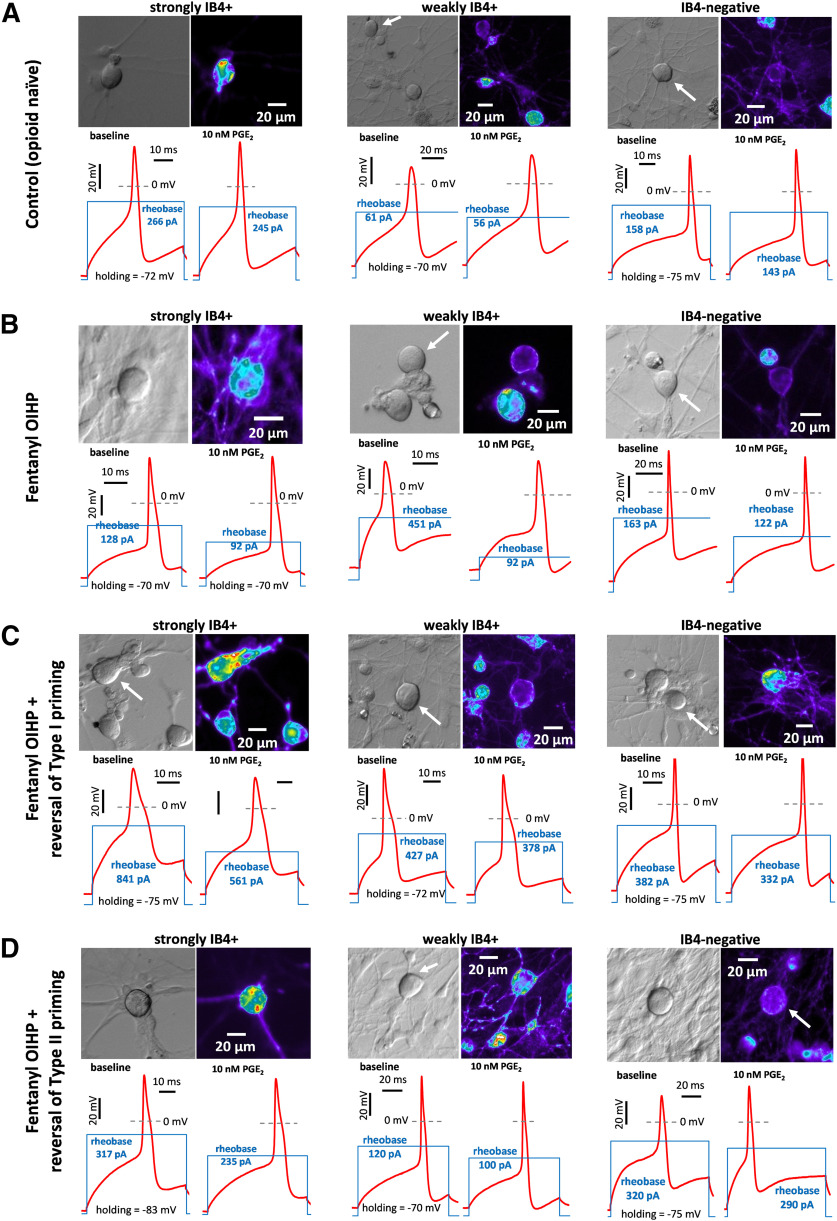
Figure 4.
Illustration of PGE2-induced sensitization in small DRG neurons in vitro. Rows (A–D) represent groups of DRG neurons cultured from rats with different conditions: control (opioid naive, A), fentanyl-primed (B), and fentanyl-primed with reversal of Type I (C) and of Type II (D) priming, as defined in Figures 5–7. Strongly IB4+, weakly IB4+, and IB4– small DRG neurons, sensitized by PGE2, are depicted in each group. For each depicted neuron, its image in transmitted light (DIC contrast; upper left), fluorescent image of IB4-labeling (pseudocolor; upper right), and two electrophysiological recordings (below) are shown. The recordings, made in current clamp mode, show APs (red line) induced by current step of rheobase magnitude, before (lower left) and 10 min after (lower right) administration of PGE2 (10 nm). Stimulation profile is shown as blue line, in the same scale in left and right recordings (the scale differs between neurons). Note, the reduction in rheobase after administration of PGE2, which was used to quantify magnitude of sensitization (further analyzed in Figs. 5–7), is larger in fentanyl-primed group for each IB4-binding status (B) compared with opioid naive group (A); attenuation of the sensitizing effect of PGE2 was observed in both reversal groups (C, D) compared with the primed group (B), in weakly IB4+ and IB4–, but not in strongly IB4+ neurons.