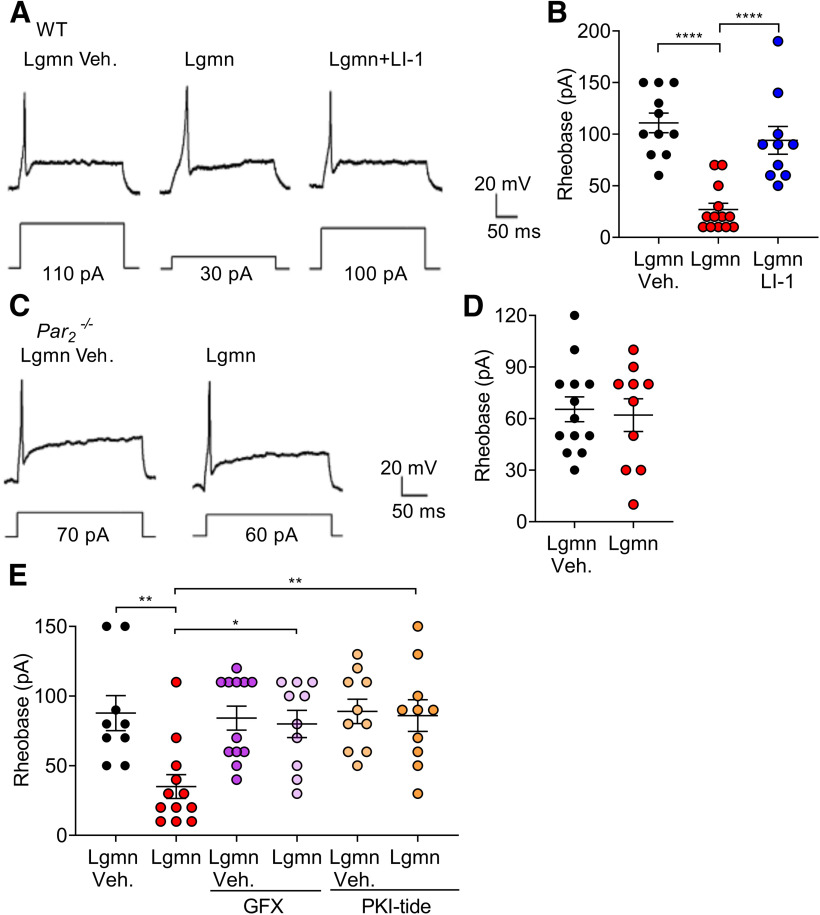
Figure 6.
PAR2 mediated Lgmn-induced hyperexcitability in TG neurons. A, Representative raw traces of whole-cell patch-clamp recordings showing membrane potential response at rheobase of TG neurons from WT mice treated with Lgmn vehicle, Lgmn, and Lgmn + LI-1. B, Rheobase of TG neurons in different treatment groups. Lgmn vehicle: 110.0 ± 31.4 pA, n = 11; Lgmn: 26.9 ± 22.1 pA, n = 13; Lgmn + LI-1: 94.0 ± 42.4 pA, n = 10 (F(2,31) = 23.14, ****p = 1.23E-6, when Lgmn and Lgmn vehicle are compared, ****p = 6.93E-5, when Lgmn and Lgmn + LI-1 are compared, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons). C, Representative raw traces of whole-cell patch-clamp recordings showing membrane potential response at rheobase of TG neurons from Par2−/− mice treated with Lgmn and Lgmn vehicle. D, Rheobase of TG neurons from Par2−/− mice. Lgmn vehicle: 65.3 ± 26.0 pA, n = 13; Lgmn: 62.0 ± 30.1 pA, n = 10. E, Lgmn induced hyperexcitability and PKC-dependent or PKA-dependent pathways. Perforated patch-clamp recordings were used to measure rheobase of TG neurons. Neurons were preincubated with GFX 1 μm and PKI-tide 1 µm before Lgmn or Lgmn vehicle treatments. Rheobase was measured after neurons were challenged with Lgmn and Lgmn vehicle. Lgmn vehicle, 87.7 ± 12.5 pA, n = 9; Lgmn, 35.6 ± 8.5 pA, n = 12; GFX + Lgmn vehicle, 84.1 ± 8.5 pA, n = 12; GFX + Lgmn, 80.0 ± 9.7 pA, n = 10; PKI-tide + Lgmn vehicle, 89.0 ± 8.7 pA, n = 10; PKI-tide + Lgmn, 86.0 ± 11.3 pA, n = 10 (F(5,57) = 4.93, **p = 0.0052, when Lgmn and Lgmn vehicle are compared, *p = 0.0198 when the Lgmn and Lgmn + GFX are compared, **p = 0.0198, when Lgmn and Lgmn + PKI-tide are compared, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons).