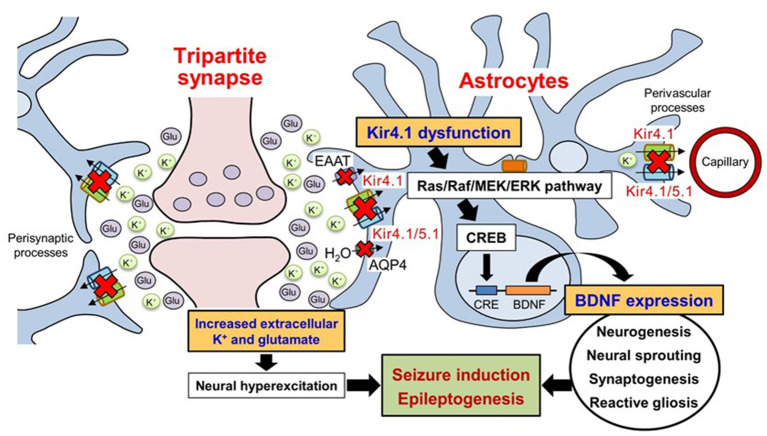
Figure 3.
Schematic drawing illustrating the effects of Kir4.1 dysfunction on neural hyperexcitation and astrocytic BDNF expression. Dysfunction (genetic mutation, down-regulated expression, and pharmacological blockade) of Kir4.1 channels increases extracellular K+ and glutamate at synapses and causes neural hyperexcitability. The dysfunction of Kir4.1 channels activates the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and facilitates BDNF expression in astrocytes. Based on these changes, astrocytic Kir4.1 channels play important roles in modulating seizure induction and epileptogenesis. Modified from Ohno et al. (25).