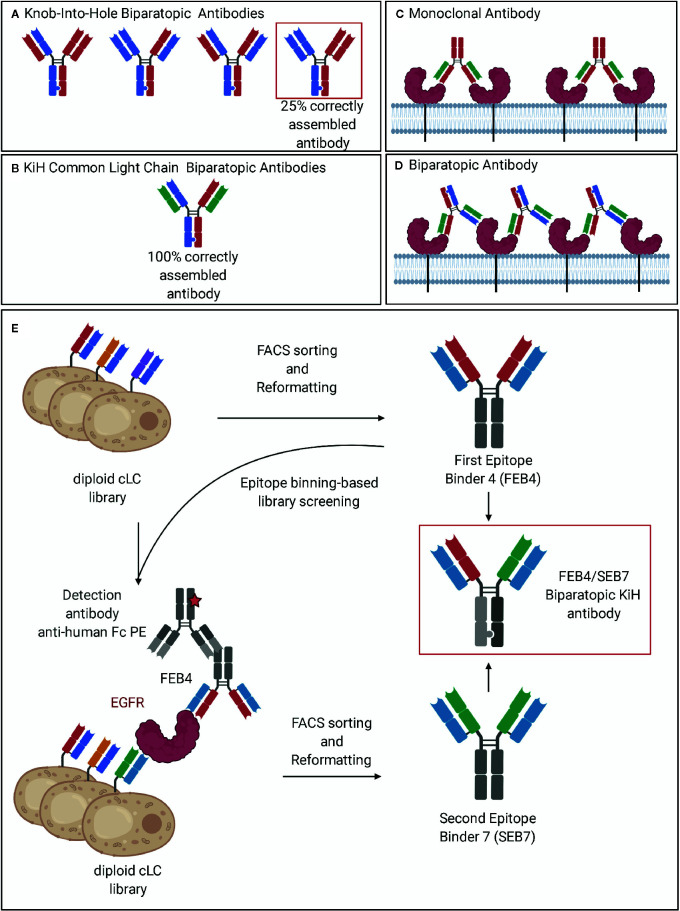
Figure 1.
Common light chain biparatopic antibodies and schematic representation of the screening procedure. (A) The heterodimerization of the heavy chains is achieved by the Knob-into-Hole technology. Due to the need for correct pairing of heavy and light chains, only 25% of produced antibodies are correctly assembled. (B) The utilization of a common light chain pairing with both heavy chains enabled the circumvention of the light chain pairing problem. (C) Monoclonal antibodies recognize a single epitope of the target antigen and can therefore bind to two individual receptors. (D) Biparatopic antibodies bind to two distinct epitopes of the same antigen. By binding to two receptor molecules, additional epitopes on the target remain exposed allowing for the binding of an additional antibody, leading to crosslinking of the target receptor and receptor clustering. (E) Epitope binning-based FACS screening resulted in two VH domains, addressing orthogonal epitopes while comprising one common light chain. Subsequent reformatting into the Knob-into-Hole format enabled the production of a biparatopic antibody. Created with BioRender.com.