Figure 7.
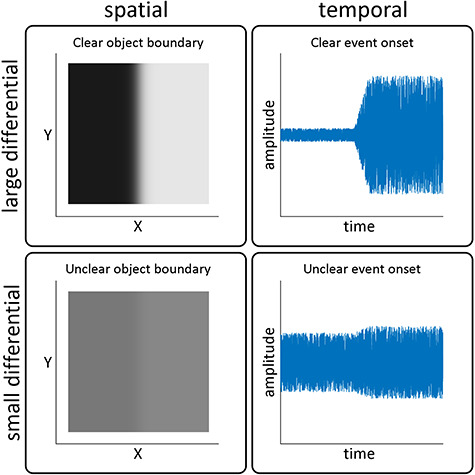
Abrupt increases of stimulus intensity are the temporal equivalent of spatial edges. Left column: representative plots of a spatial edge with large differential intensity (high contrast, top) and small differential intensity (low contrast, bottom). The large differential results in a sharper and more clearly defined edge, which identifies an object with higher certainty. Right column: abrupt increases of auditory intensity with large (top) and small (bottom) differentials. As in the visual domain, a larger differential results in a sharper, more clearly defined edge, albeit in time rather than in space. A sharper temporal edge identifies the occurrence of an event with higher certainty.
