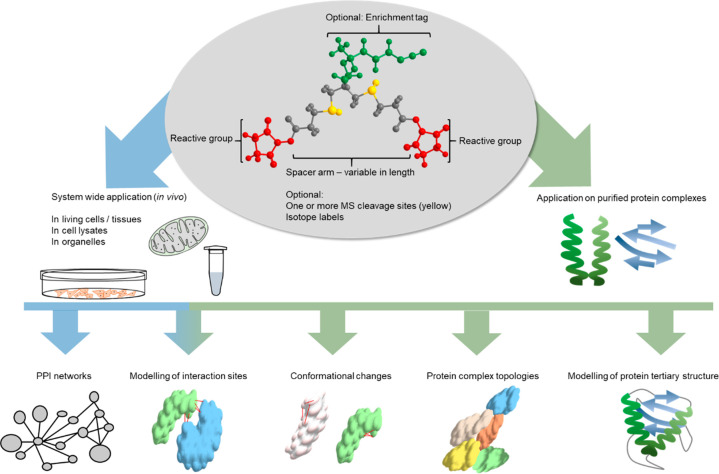
Figure 1.
Applications of XL-MS. A cross-linker consists of three main elements: First, the reactive group either targets specific amino acid residues or nonspecifically reacts with any amino acid. Second, the spacer arm might contain one or more labile sites for MS cleavability. Shorter spacers provide higher resolution structural data but will lead to fewer cross-links. Third, some reagents bear an enrichment handle for the selective capture of cross-linked peptides. The linker molecule can be applied either to single proteins/protein complexes (shown in green) or in vivo (shown in blue). After MS/MS acquisition and data analysis, the obtained cross-links can give valuable information on the protein structure, complex topologies, conformational changes, specific interaction sites, or (proteome-wide) protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks.