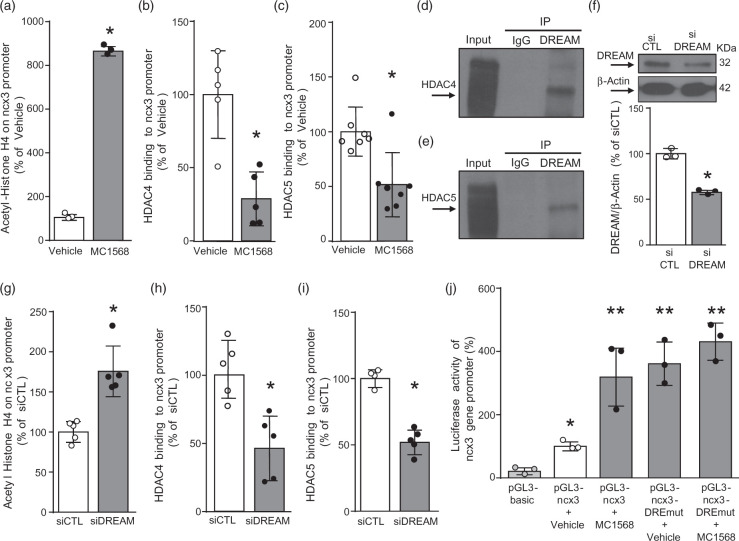
Figure 3.
HDAC4 and HDAC5 bound to ncx3 brain promoter via downstream regulatory element antagonist modulator (DREAM).
(a–c) ChIP analysis of the ncx3 brain promoter performed with: (a) anti acetylated-histone H4, (b) anti-HDAC4, and (c) anti-HDAC5 in cortical neurons. Acetylation status of histone H4 (n = 3) and binding activity of HDAC4 (n = 5) and HDAC5 (n = 7) are graphically represented as the percentage of vehicle. *p ≤ 0.05 versus vehicle, Student t test. (d, e) Representative Western blot showing immunoprecipitation between DREAM and HDAC4 and between DREAM and HDAC5 in cortical neurons. IgG was used as a negative control. (f) Representative WB with quantification in cortical neurons after 24 h of transfection with siDREAM (n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus siCTL, Student t test. (g–i) ChIP analysis of the ncx3 brain promoter performed with: (g) anti-acetylated-histone H4, (h) anti-HDAC4, and (j) anti-HDAC5 in cortical neurons. Acetylation status of histone H4 (n = 5) and binding activity of HDAC4 (n = 5) and HDAC5 (n = 4/5) are graphically represented as the percentage of siCTL. *p ≤0.05 versus siCTL, Student t test. (j) Luciferase activity of ncx3 gene promoter wild type (pGL3-ncx3) or mutated in DRE-site (pGL3-ncx3-DREmut), with or without MC1568 (5 μM), in cortical neurons (n = 3). *p ≤ 0.05 versus pGL3basic; **p ≤ 0.05 versus pGL3basic and pGL3-ncx3 + vehicle, one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.