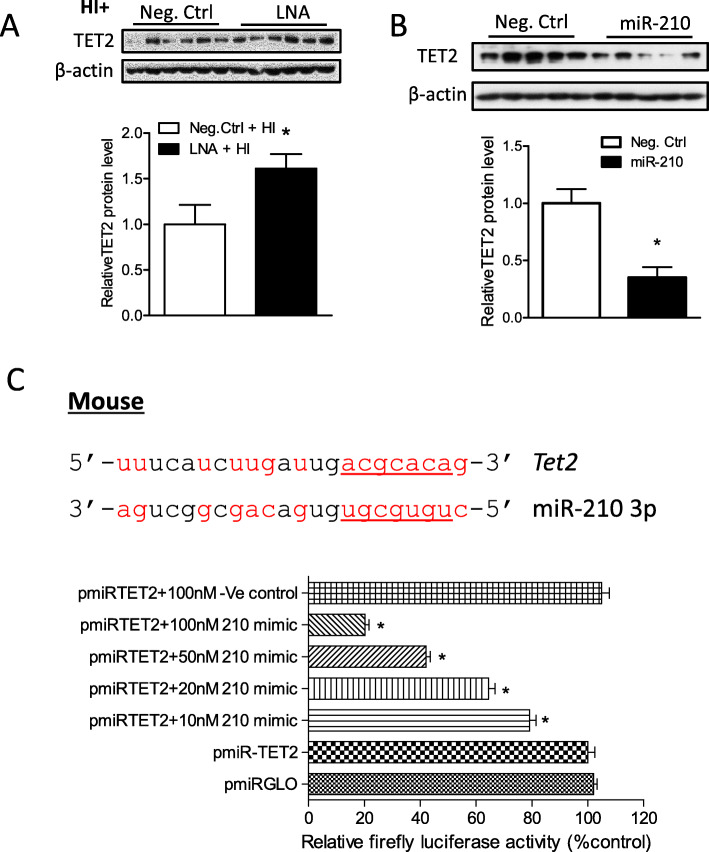
Fig. 2.
MiR-210 downregulated TET2 in the neonatal brain. a HI brain injury was induced in P7 mouse pups. Either miR-210-LNA (100 pmol) or scramble LNA (Neg. Ctrl) was administered into the ipsilateral hemisphere via i.c.v. injection 24 h prior to HI. a TET2 protein abundance was detected in the ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere of the brain 12 h after HI. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 6 pups/group. *p < 0.05 vs HI + Neg. Ctrl. b Either miR-210 mimic (100 pmol) or scramble (Neg. Ctrl) was administered into the right hemisphere of mouse brain via i.c.v. injection. TET2 protein level was detected by Western blot in the ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere of the brain 48 h after injection. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 5 pups/group. *p < 0.05 vs Neg. Ctrl. c Luciferase reporter gene assay of miR-210 targeting TET2 3′UTR. The diagram shows TET2 mRNA 3′UTR with the binding sites of miR-210 in mouse species. The pmirGLO plasmid inserted with TET2 3′UTR sequence containing putative miR-210 binding sites (pmiRTET2) was transfected into PC12 cells and was treated with either miR-210 mimics or scramble (Ve-control). Firefly and Renilla reniformis luciferase activities were measured in a luminometer using a dual-luciferase reporter assay system. *p < 0.05, treatment vs Ve control