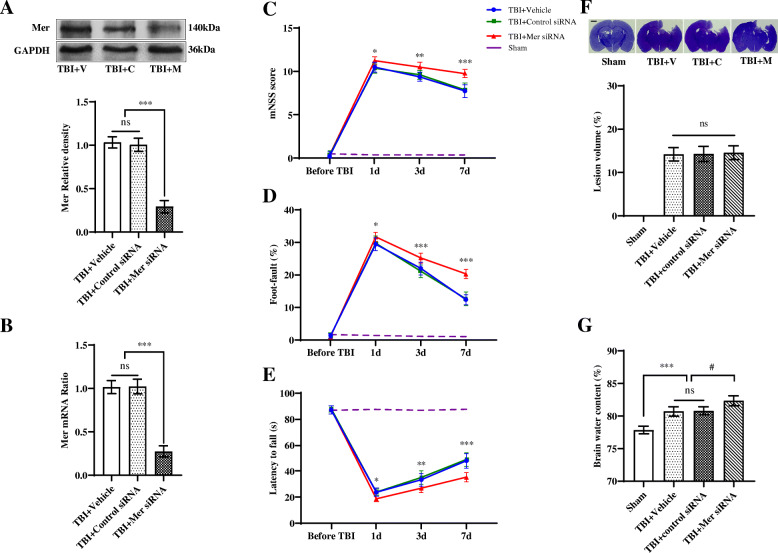
Fig. 3.
In vivo knockdown of Mer worsened the functional outcomes after TBI. a Western blot was used to assess the knockdown efficacy of Mer siRNA. Representative immunoblots and quantification showing Mer siRNA inhibited the expression of Mer protein in the injured cortex at 3 days post-TBI. TBI + vehicle: TBI + V, TBI + control siRNA: TBI + C, TBI + Mer siRNA: TBI + M. GAPDH: loading control. Data are expressed as fold change compared to the TBI + V group; n = 6 mice per group. b Quantitative RT-PCR analysis also showing Mer siRNA significantly inhibited the expression of Mer mRNA in the injured cortex at 3 days post-TBI. Data are expressed as fold change compared to the TBI + V group; n = 6 mice per group. c–e Modified neurological severity scores (mNSS) (c), foot-fault test (d), and rotarod test (e) were performed before and 1, 3, and 7 days after TBI. n = 8 mice per group. f Quantification of TBI-induced lesion volume at 3 days post-insult. n = 6 mice per group. Scale bar = 1 mm. g Cerebral edema was measured by brain water content. Mer siRNA significantly elevated brain edema level at 3 days post-injury, when compared to both the vehicle and control siRNA group. n = 8 mice per group. In a–g, data are presented as mean ± SD; *, #, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, nonsignificant, p > 0.05. In a, b, f, g, one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc tests. In c–e, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc tests