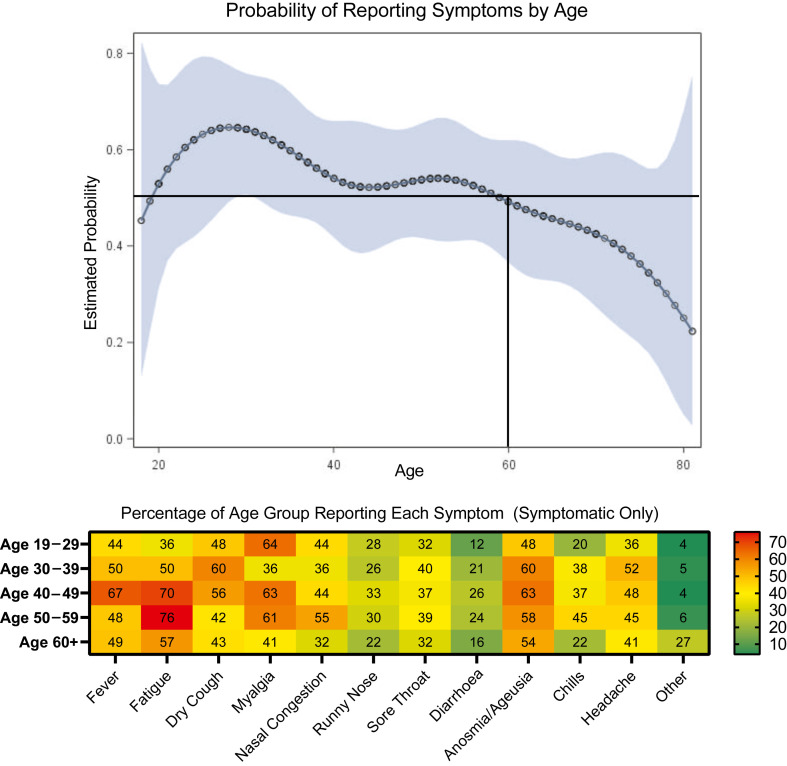
Fig. 4.
Reported symptoms of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection by age. (Top) Probability and confidence band of reporting symptoms by age for individuals testing positive for active or past SARS-CoV-2 infection in New Orleans and Baton Rouge, Louisiana. The probability of reporting symptoms by age was modelled using a logistic regression with cubic splines and four nodes. Older individuals (>60 years) had decreasing probability of reporting symptoms as age increased. The highest probability of reporting symptoms was 64.6% (50.4%–76.5%) at age 29 years which decreased to a probability of 49.3% (36.6%–62.0%) at age 60 and only 25.1% (5.0%–68.1%) at age 80. (Bottom) Percentage of symptomatic individuals reporting each symptom by age group with an overlaid heatmap to indicate the relative detectability of each symptom in each age group.