Figure 1.
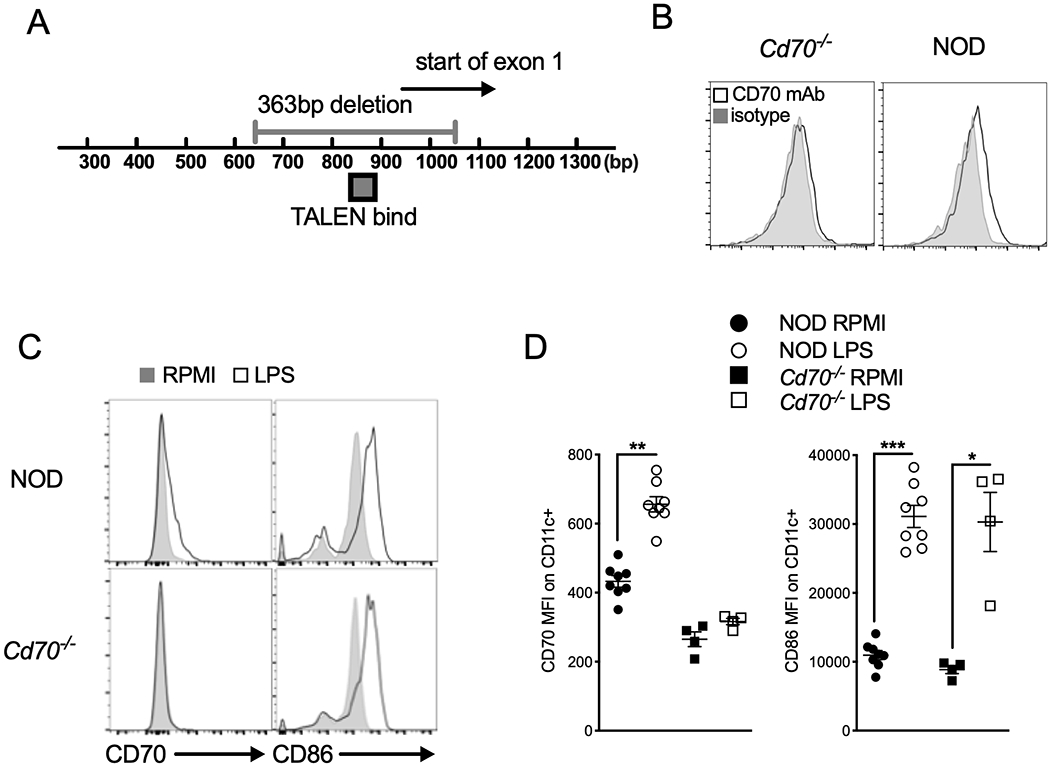
Cd70 gene disruption in NOD mice using transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs). (A) Genomic map showing the TALEN binding site used to create a 363 bp deletion in Exon 1. Numbers below the bar represent the base-pair (bp) location from the Cd70 start site. (B) Absence of CD70 expression confirms its deletion in Cd70−/− mice. Splenocytes from Cd70−/− and standard NOD mice were incubated for 24 h with 1 μg/ml LPS, after which cells were harvested and analyzed for CD70 protein expression by flow cytometry. Representative histograms show CD70 and isotype control staining on CD11c+ DCs. (C & D) Upregulation of CD86 is not affected by Cd70 ablation. Flow cytometric analysis of CD70 and CD86 expression on CD11c+ cells among Cd70−/− and WT NOD splenocytes cultured with complete media alone (RPMI) or LPS for 24 hours. (C) Representative histograms show the expression of CD70 and CD86 on CD11c+ gated cells. (D) Graphs show summarized data for MFI of CD70 and CD86 Ab staining on CD11c+ DCs. Results are shown as mean ± SE from 4–8 individual mice per group. Statistical analysis was carried out by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
