Figure 8.
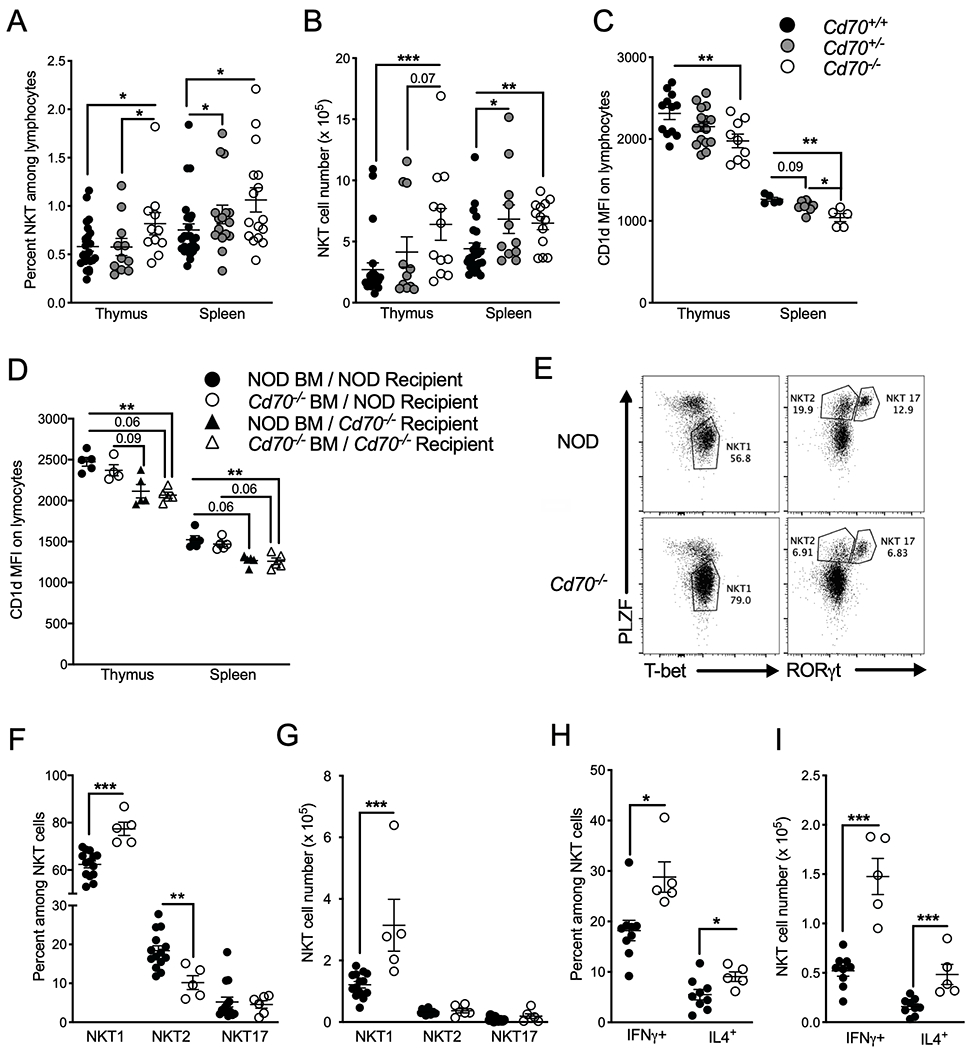
CD70 regulates iNKT cell development and function. The frequency (A) and number (B) of thymic and splenic CD1d tetramer+ TCRβ+ iNKT cells in 7- to 10-wk old female mice of the indicated genotypes. (C) MFI of CD1d Ab staining of thymocytes and splenocytes from 7- to 10-wk old female mice of the indicated genotypes. (D) Thymic and splenic CD1d expression in NOD and Cd70−/− mice 8 weeks after lethal irradiation and reconstitution with BM cells from CD70-deficient or -intact mice. (E) Characterization of thymic iNKT cell subsets by flow cytometric analysis of the key transcription factors PLZF, T-bet, and RORγt. (F) Frequency and (G) number of iNKT1 (T-bet+ PLZFlo), iNKT2 (PLZFhi RORγt−) and iNKT17 (PLZFhi RORγt+) iNKT cells from 7- to 8-week-old female NOD and Cd70−/− thymi. (H & I) Intracellular IFNγ and IL4 staining of iNKT cells resident in spleens of 7- to 8-wk old NOD and Cd70−/− mice injected i.v. 2 h previously with 4 μg per mouse of α-GalCer or DMSO. (H) Frequency and (I) number of IFNγ and IL4 producing iNKT cells after α-GalCer treatment. Data represent results from two independent experiments analyzed by Mann-Whitney test; error bars correspond to mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Actual P values are provided when 0.1>p-value>0.05.
