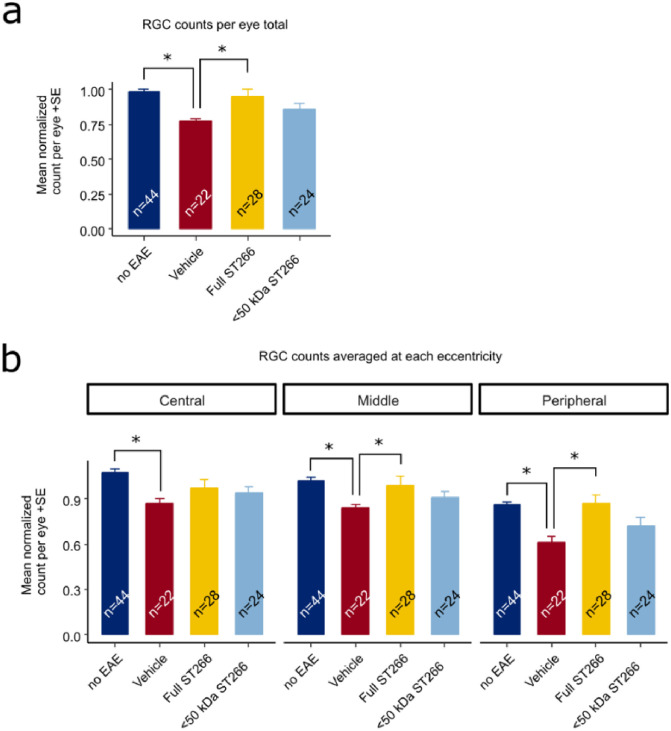
Fig 6. ST266 attenuates RGC loss in mice with mild-moderate EAE optic neuritis.
Retinas were isolated from the eyes of control mice and EAE mice with mild-moderate EAE disease and immunolabeled with Brn3a. Data are from the same eyes shown in Fig 5, with the exception of one eye from the vehicle (PBS)-treated EAE mouse cohort in which the retina was damaged during dissection and therefore could not be quantified. (a) The average normalized RGC count across the entire retina shows a decrease in RGC numbers in vehicle-treated EAE mouse eyes (n = 22 eyes) compared to eyes from non-EAE control mice (n = 44 eyes) (*p<0.05). RGC numbers were significantly higher in eyes from ST266-treated EAE mice (n = 28) as compared with PBS-treated EAE mice (*p<0.05), whereas treatment with <50 kDa ST266 (n = 24 eyes) led to a non-significant trend towards increased RGCs. (b) RGC numbers in central, mid-peripheral and peripheral regions of the retina showed a significant decrease in all regions in eyes of PBS-treated EAE mice as compared with control mouse eyes, and treatment with daily intranasal ST266 improved RGC survival in both the mid-peripheral and peripheral retinal regions (*p<0.05). Data shown as mean +SEM.