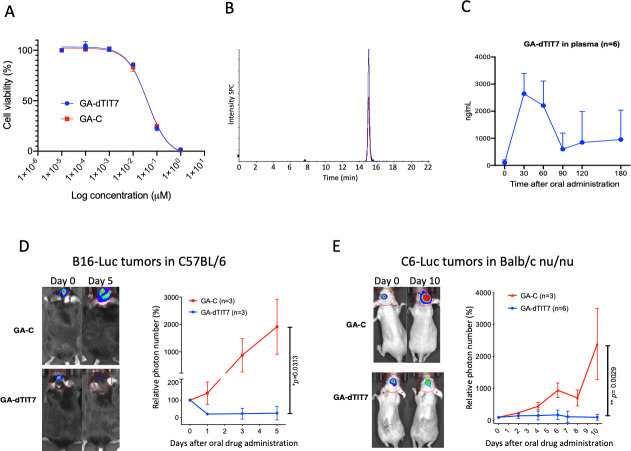
Fig 6. Therapeutic effect of orally-administered GA-dTIT7 on brain tumors.
A. Mouse melanoma B16 cells were treated with reagents shown at indicated concentrations, cultured 2 days, and assessed for viability using a CellTiter Glo (Promega) assay. The IC50 of each reagent was determined using GraphPad Prism software. B. Quantitative analysis of GA-dTIT7 in mouse plasma by LC-MS/MS. Plasma from GA-dTIT7-injected C57BL/6 female mice (9 μL) were combined with 1 μL GA-isodTIT7 (1.0 μg), immediately mixed with 40 μL cold acetone, and then centrifuged to remove precipitates. The supernatant was then applied to LC-MS/MS, and eluates monitored by m/z 1725 for GA-isodTIT7 (blue) and m/z 1719 for GA-dTIT7 (red). C. GA-dTIT7 levels in plasma from mice-orally administered GA-dTIT7. Each C57BL/6 mouse was administered 1 mg GA-dTIT7. GA-dTIT7 levels were determined by LC-MS/MS, as shown in B. D. B16-Luc cells were injected into the brain of C57BL/6 mouse and tumor growth was monitored by IVIS imaging. When photon number reached 2 x10^4 (approximately 5 days after inoculation), GA-dTIT7 (1.16 μmoles or 2 mg) or the molar equivalent GA-C (control) diluted with 10% TDC (200 μl) was orally-administered daily for 5 days. Left panels show representative control and experimental mice imaged 0 and 5 days after drug administration. Photon number is quantified at right. E. C6-Luc cells were injected into the brain of C57BL/6 mice and tumor growth monitored by IVIS imaging. When photon number reached 2 x10^4 (approximately 10 days after C6-Luc cell inoculation), GA-dTIT7 and control GA-C were orally administered daily for 10 days. Left panels show representative control and experimental mice imaged 0 and 10 days after drug administration. Photon number is quantified at right. In these graphs, error bars denote means ± SEM. Statistical analysis was assessed by Student's t-test.