Fig. 4. Polarization-sensitive SRS imaging of ghost RBCs at 2850 cm−1 and various AmB-treated fungal species at 1556 cm−1.
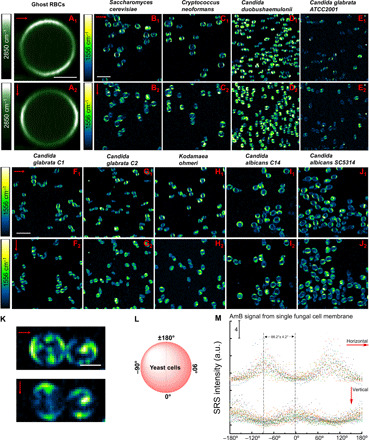
(A1 and A2) SRS images of ghost RBCs at 2850 cm−1 in the horizontal and vertical polarization directions, respectively. Pump, 802 nm; Stokes, 1040 nm. Pixel dwell time: 50 μs. Scale bar, 2.5 μm. (B1 to J1) SRS images of AmB-treated S. cerevisiae AR-399, C. neoformans, C. duobushaemulonii AR-0394, C. glabrata ATCC2001, C. glabrata C1, C. glabrata C2, K. ohmeri AR-0396, C. albicans C14, and C. albicans SC5314 at 1556 cm−1 with laser polarization in the horizontal direction. Pump, 895 nm; Stokes, 1040 nm. Pixel dwell time: 50 μs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B2 to J2) SRS images of the same strains but with laser polarization in the vertical direction. Pump, 895 nm; Stokes, 1040 nm. Pixel dwell time: 50 μs. Scale bar, 10 μm. (K) Zoom-in view of AmB-treated C. neoformans under two laser polarization directions. Scale bar, 2.5 μm. (L) Schematic of fungal cell membrane with angles defined. (M) Quantitative analysis of SRS signal intensity of single fungal cell at 1556 cm−1 under two laser polarization directions. AmB: 3.2 μg/ml, 1-hour treatment at 30°C. Laser orientation is indicated by red arrows.
