Figure 2.
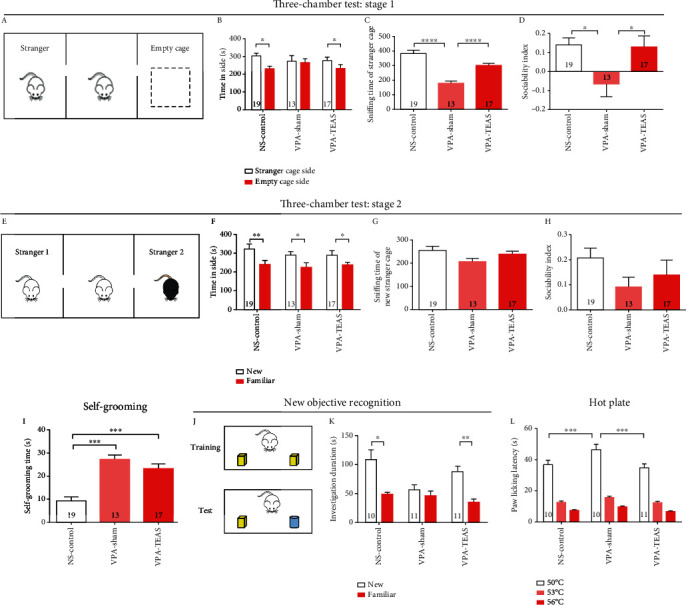
TEAS treatment in early life stage had long-term behavior effects on offspring of VPA treated rats. (a) Schematic diagram of three-chamber test in stage 1 (social preference). (b) The time the animal spent investigating either on the stranger cage side or empty cage side in stage 1 of the three-chamber test (paired t-test, NS-control n = 19, VPA-sham n = 13, VPA-TEAS n = 17). (c) The sniffing time of the stranger cage in stage 1 of the three-chamber test (one-way ANOVA). (d) The social preference index (one-way ANOVA). (e) Schematic diagram of the three-chamber test in stage 2 (social novelty). (f) The time spent investigating either the new stranger or the familiar stranger in stage 1 of the three-chamber test (paired t-test, NS-control n = 19, VPA-sham n = 13, VPA-TEAS n = 17). (g) The sniffing time on new stranger in stage 2 of the three-chamber test (one-way ANOVA). (h) The social preference index (one-way ANOVA). (i) The time of self-grooming test (one-way ANOVA, NS-control n = 19, VPA-sham n = 13, VPA-TEAS n = 17). (j) Schematic diagram of new objective recognition. (k) The time spent on investigating either familiar or novel object in novel object recognition test (one-way ANOVA, NS-control n = 10, VPA-sham n = 10, VPA-TEAS n = 11). (l) The withdrawal latency in the hot plate test for heat sensitivity (one-way ANOVA for same temperature, NS-control n = 10, VPA-sham n = 10, VPA-TEAS n = 11). Data was presented as the mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.
