Fig. 1.
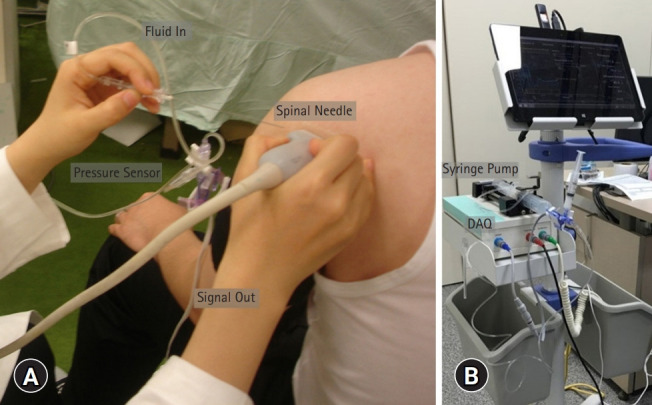
Experimental setup for capsule-preserved hydraulic distension (A) with real-time pressure monitoring (B). While the patient is comfortably seated upright on a stool, a 3.5-inch 22-gauge spinal needle is inserted 1 cm lateral to the ultrasound transducer and advanced into the posterior intraarticular space under ultrasound guidance. The pressure sensor is connected to manometric tubes via a 3-way stopcock so that the pressure in the tubes can be measured by the sensor while fluid is infused via the syringe pump. The signal from the sensor is digitalized by a data-acquisition device (DAQ).
