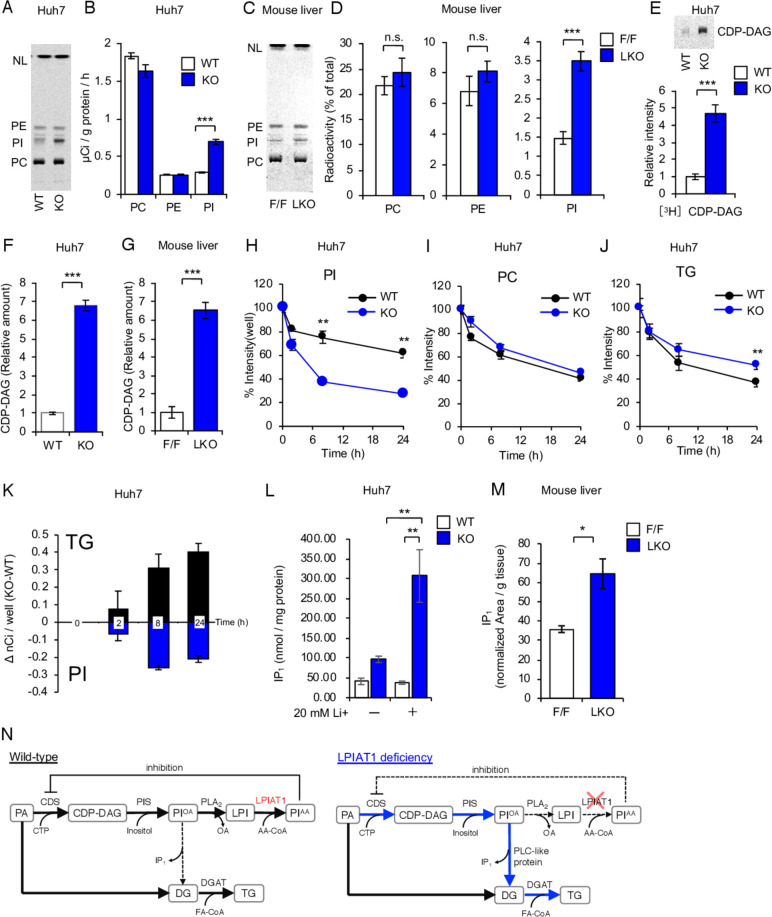
Figure 3.
PI-derived diacylglycerol flow into TG synthesis. (A, B) Phospholipid synthesis speed measured by incorporation of [14C]glycerol into each phospholipid species for 2 hours. (A) Representative image of TLC separation of total lipids from WT or KO cells. (B) Radioactivity of each phospholipid fraction (n=4). (C, D) Phospholipid synthesis speed measured by incorporation of intraperitoneally injected [14C]glycerol (0.133 mCi/kg body weight) into liver phospholipid species of 18–20 weeks-old male F/F or LKO mice. (C) Representative image of TLC separation of total lipids from F/F or LKO mice liver. (D) Radioactivity of each phospholipid fraction (n=5). (E) CDS activity measured by the incorporation of [3H]CTP into CDP-DAG for 2 hours. Total lipids from WT and KO Huh-7 cells were separated by TLC and the radioactivity of CDP-DAG fraction were measured (n=4). (F) Amounts of CDP-DAG in WT and KO Huh-7 cells (n=3). (G) Amounts of CDP-DAG in F/F and LKO mice liver (n=3) (H–J) lipid degradation measured by the reduction of [14C]glycerol radioactivity from each lipid fraction of cells pre-incubated with [14C]glycerol for 12 hours and then shifted to [14C]glycerol-free medium at indicated time point. Radioactivity of PI (H), PC (I) and TG (J) fractions were measured. data were shown by the relative ratio of signal intensity, with the value at 0 hour set as 100% (n=3). (K) Changes in the radioactivity of PI and TG during Chase analysis. Reduction of radioactivity from 0 hour was shown at each time point (n=3). (L) Amount of cellular inositol monophosphate in WT and KO Huh-7 cells treated with or without 20 mM Li+ for 2 hours (n=3). (M) Amounts of inositol monophosphate in F/F and LKO mice liver intraperitoneally injected with 250 mM Li+for 3 hours (F/F, n=3; LKO, n=5) (N) A schematic diagram of the mechanism for the increase in TGs synthesis after depletion of LPIAT1. Values are shown as mean±SEM data were analysed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (L) or unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (B, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, M): *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. ANOVA, analysis of variance; CDP-DAG, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol; CDS, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol synthase; DGAT, diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase; DG, diacylglycerol; FA, fatty acid; IP1, inositol monophosphate; KO, knockout; LPI, lysophosphatidylinositol; LKO, hepatocyte-specific Lpiat1 knockout; LPIAT1, lysophosphatidylinositol acyltransferase 1; NL, neutral lipid; n.s., not significant; PA, phosphatidic acid; PIOA, phosphatidylinositol with oleic acid; PIAA, phosphatidylinositol with arachidonic acid; PIS, PI synthase; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PLC, phospholipase C; TG, triglyceride; WT, wild-type.