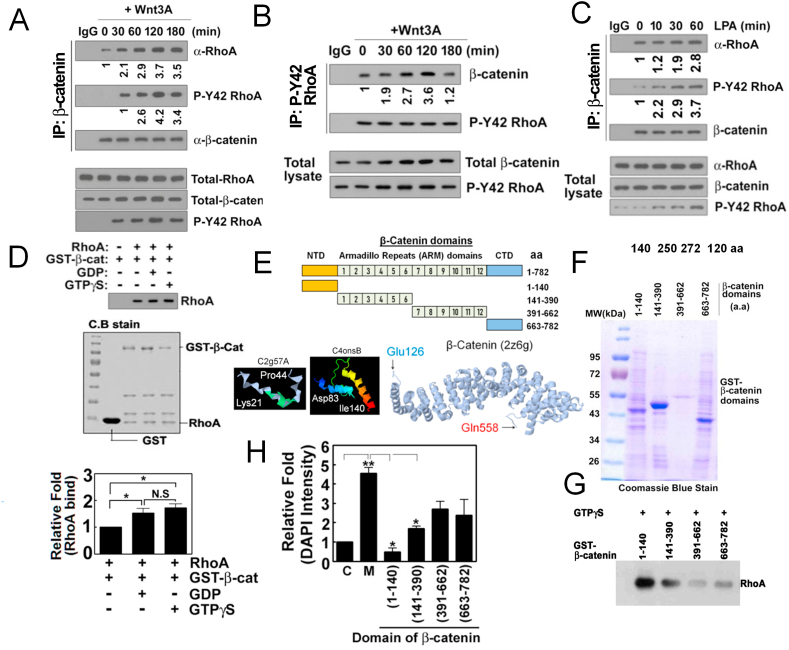
Fig. 4.
β-Catenin interacts with p-Tyr42 RhoA in response to Wnt3A. (A, B) HEK293T cells (2–5x105) were stimulated with Wnt3A (30 ng/ml), β-catenin and p-Tyr42 Rho were immunoprecipitated from cell lysates and co-immunoprecipitated RhoA and β-catenin were detected by western blotting (A and B, respectively). (C) LPA (10 μM) was treated to HEK293T cells and β-catenin was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates and co-immunoprecipitated RhoA and p-Tyr42 RhoA were detected by western blotting. (D) Recombinant purified RhoA (0.1 μg/50 μl) was preloaded with GDP or GTPγS for 30 min and then was incubated with GST-β-catenin (0.1 μg/50 μl) for 2 h. RhoA associated with GST-β-catenin was detected by western blotting. (E) Schematic of the domains and partial 3D structure of β-catenin are shown. (F) Recombinant purified domains of β-catenin were run with SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie-blue. (G) RhoA associated with several domains of GST-β-catenin was detected by western blotting. (H) Cells were transfected with plasmid DNAs of various domains of β-catenin and cell proliferation stimulated by Wnt3A (30 ng/ml) was assayed by DAPI staining. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)