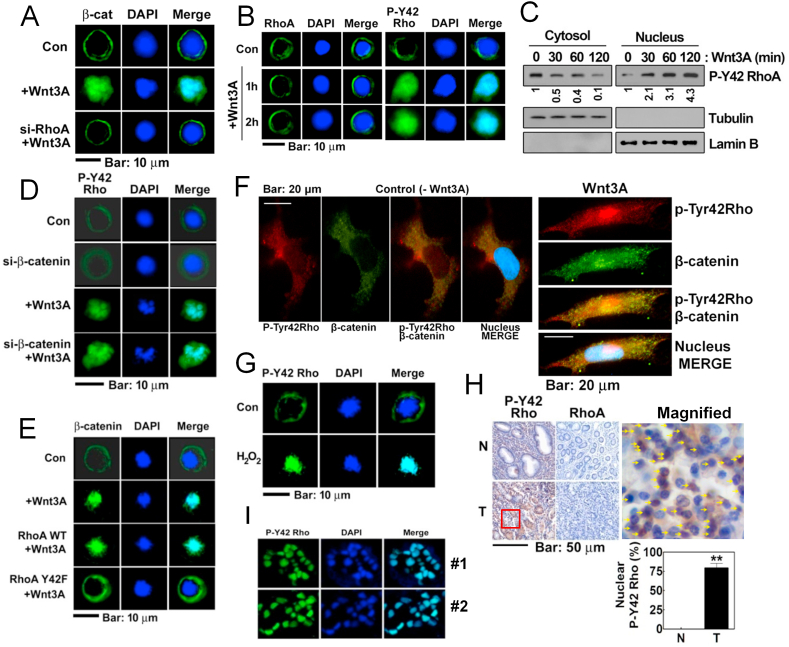
Fig. 7.
P-Tyr42 RhoA is localized to the nucleus upon Wnt3A. (A) HEK293T cells were transfected with si-RhoA and then treated with Wnt3A (30 ng/ml) for 2 h. Localization of β-catenin was assessed by immunofluorescences assay (green) and nucleus was stained with DAPI. (B) Localization of RhoA and p-Tyr42 Rho were assessed in HEK293T cells stimulated by Wnt3A. (C) Cells were stimulated with Wn3A and cytosolic and nuclear p-Tyr42 Rho proteins were detected after each fraction preparation. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with si-β-catenin (10 nM) for 72 h and p-Tyr42 Rho levels were then assessed (green). (E) HEK293T cells were transfected with RhoA WT and RhoA Y42F, then the cells were stimulated with Wnt3A, and the localization of β-catenin was assessed as above. (F) 293 A cells of flattened large shape were treated with Wnt3A (50 ng/ml) for 30 min and p-Tyr42 Rho (red) and β-catenin (green) were visualized with immunohistochemical method. (G) HEK293T cells were stimulated with 100 μM H2O2 for 2 h and localization of p-Tyr42 Rho was assessed. (H) Human stomach cancer tissues were stained with p-Tyr42 Rho antibody and the p-Tyr42 Rho presence in the nucleus were scored. Yellow arrows indicate cells containing nuclear p-Tyr42 Rho. (I) Immunofluorescence staining of human stomach cancer tissues with p-Ty42 Rho antibody was performed. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)