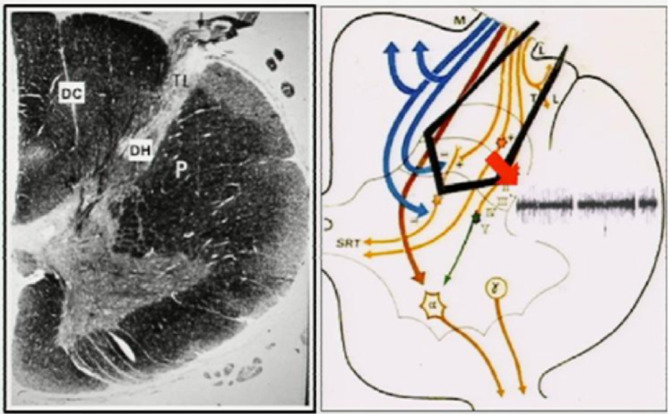
Fig. 1.
Organization of fibers on transverse section. Most of the fine (nociceptive) afferents, which convey excitatory input, enter the dorsolateral sulcus as a lateral bundle of the DREZ, then penetrate the dorsal horn (DH) ventrolaterally through the medial part of the tract of Lissauer (TL) and the dorsal aspect of the substantia gelatinosa (SG). The Ramón y Cajal’s recurrent collaterals of the large primary afferent fibers approach the DH through the ventromedial aspect of the SG to exert inhibitory effects on the DH neurons [75]. Because a number of dendrites of the cells of origin of the spinoreticulothalamic tract, which will form the contralateral anterolateral pathways, make synaptic connections with the primary afferents inside the SG layers, the SG exerts a strong segmental modulating effect on the nociceptive input.80 Arrowhead: The microsurgical DREZotomy (MDT) target includes the lateral bundle of the (nociceptive) fine fibers, the medial (excitatory) part of the TL, and the 5 dorsalmost layers of the DH where the primary afferents terminate and whose neurons become hyperactive if deafferentated. MDT attempts to spare the máximum number of the large fibers of the medial bundle that reach the DC. Reprinted from Sindou et al. Pain 2001:92:159-71, with permission of Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc [75].