Figure 5. Dynamic folding modulation design and structural analysis of FGF21SS variant.
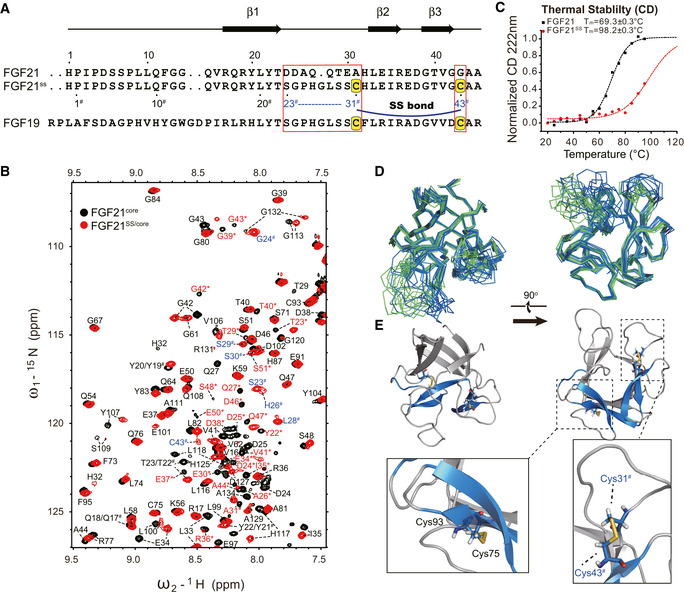
- Sequence alignment of FGF21, FGF21SS, and FGF19 in the mutated region. The mutation sites are indicated by boxes. Cysteines for disulfide bond formation are highlighted on a yellow background. The secondary structure of FGF21 is shown on the top. The N‐terminal residue IDs of FGF21SS are indicated under the sequence. # is used to identify the mutated residues (codes are colored blue) and the same residues having different sequence number in FGF21SS from wild type.
- Temperature denaturation CD experiments indicating the significant increase of thermostability. CD value was recorded and normalized at 222 nm. Tm value of the proteins is fitted using Boltzmann function.
- Superimposition of FGF21SS/core (skyblue) and FGF21core (green) structure ensembles (10 energy‐refined structures each) in ribbon representation showing the structure conservation upon SS bond mutation.
- Cartoon representation of FGF21SS/core. Cys31#‐Cys43# (between β2 and β3) and Cys75‐Cys93 (between β6 and β9) SS bonds are highlighted and shown as stick representations.
