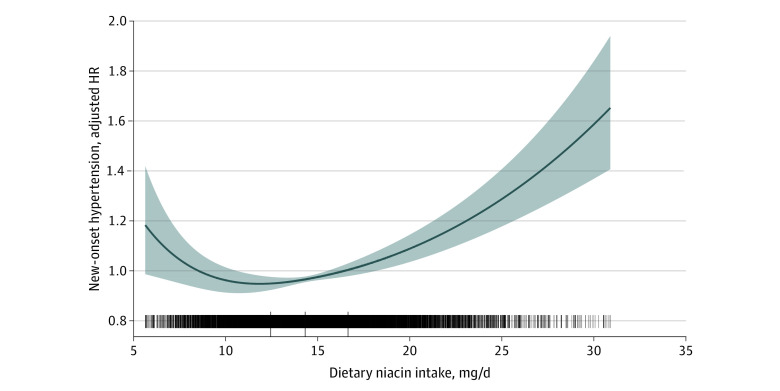
Figure 1. Dietary Niacin Intake and the Risk of New-Onset Hypertension.
The shaded area indicates 95% confidence intervals for adjusted hazard ratios (HR). The model was adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, region, education, and occupation, as well as energy intake and sodium to potassium intake ratio.