Figure 14.
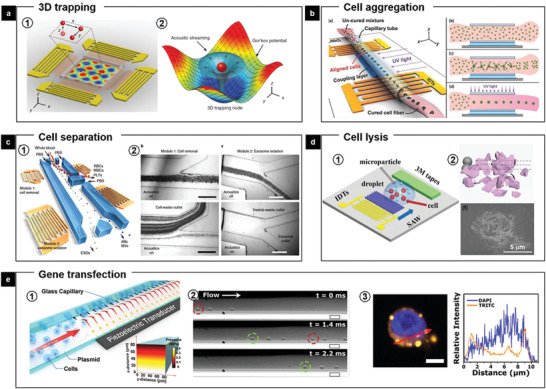
FEMs‐mediated manipulation of bioparticles including cells. a) Two pairs of IDTs are integrated with LiNbO3 crystal substrate to generate a planar standing‐wave field (a1). Numerical simulation results show the mapping of the acoustic field around a single particle (a2). Reproduced with permission.[ 101 ] Copyright 2016, National Academy of Sciences b) Schematic representation of generating a patterned cell fiber in the perpendicular orientation using SAWs. Reproduced with permission.[ 102 ] Copyright 2016, Wiley‐VCH. c) Acoustic isolation of exosomes from whole blood. Images were taken under a microscope at different separation modules. Scale bars, 500 µm. Reproduced with permission.[ 103 ] National Academy of Sciences. d1) A mechanical cell lysis device based on a SAW microchip. Schematic and d2) SEM image of the cell–magnetic microparticle collision model and a broken cell. Reproduced with permission.[ 32b ] Copyright 2019. Wiley‐VCH. e1) Schematic of the device components, where target cells undergo acoustofluidic treatment via flow through a glass capillary over a piezoelectric transducer. e2) Cells are observed to localize against a capillary wall and are pushed forward by laminar flow. e3) Intracellular delivery with fluorescently labeled DNA (TRITC channels show fluorescence signal of Cy3‐labeled DNA at the cell membrane, cytosol, and nucleus for acoustic‐treated cells). Reproduced with permission.[ 104 ] Copyright 2016, National Academy of Sciences.
