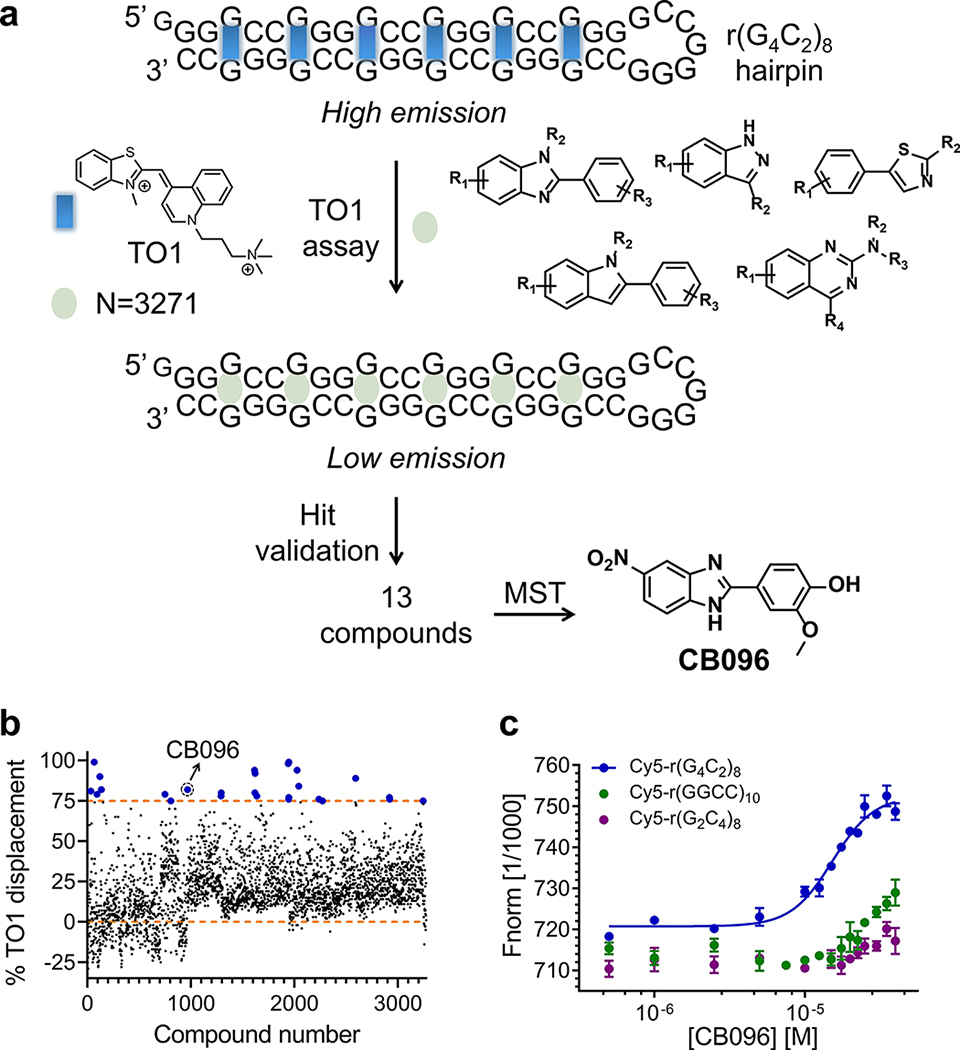
Figure 1.
Identification of CB096, a lead molecule that binds to the r(G4C2)8 hairpin. (a) Graphical representation of the two-pronged screening strategy leading to the identification of CB096. TO-PRO-1 (TO1) dye displacement assay was performed on 3271 compounds in 384-well format at 100 μM (single dose). Derivatives showing ≥75% TO1 quenching of the initial fluorescence (blue dots) were selected and further validated. A total of 13 derivatives met the criteria and were dose dependently evaluated for binding the hairpin form of Cy5-r(G4C2)8 via microscale thermophoresis (MST), of which CB096 is the best binder. (b) Results of the high throughput TO1 dye displacement assay. Compounds that exhibited ≥75% TO1 displacement were considered hits (upper orange dashed line). (c) CB096 specifically binds r(G4C2)8 (sense) over r(G2C4)8(antisense) and r(GGCC)10 (base pair) control RNAs. EC50 values were determined by plotting the changes in normalized fluorescence upon dose-dependent addition of CB096. The data points are reported as the mean values ± SD and are representative of two independent experiments each performed in duplicate.