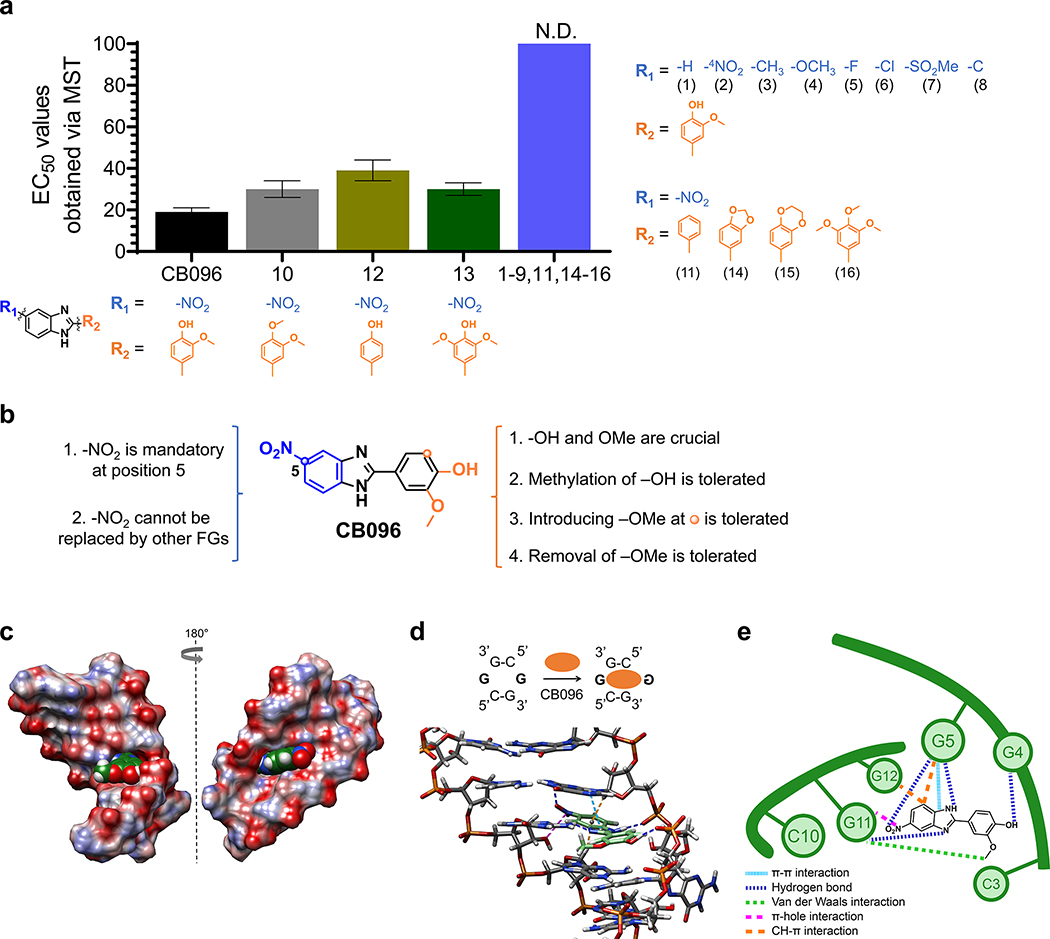
Figure 5.
Mode of binding of CB096 to 5′CGG/3′GGC motif within r(G4C2)exp hairpin revealed via SAR and MD simulations. (a) The SAR study included 17 small molecules (1–17; shown below each structure), closely related derivatives of CB096. N.D. indicates not determined. (b) Summary of the SAR study performed with 17 structurally similar derivatives of CB096. (c) Structure of CB096 in complex with the 5′CGG/3′GGC motif within the r(G4C2)-model duplex, where G represents the G residue within the 1 × 1 GG internal loop, as determined by MD simulations. Atoms of O, N, C, and H are represented in red, blue, green, and white, respectively. (d) Structure of CB096 in complex with the 5′CGG/3′GGC motif within the r(G4C2)–model duplex, highlighting the noncovalent interactions that are responsible for molecular recognition. Hydrogen (H) bonds are represented with dark blue dashed lines, π–π stacking interactions with light blue, C–H−π interactions with orange, π-hole interactions with purple, and van der Waals interactions with green dashed lines. (e) Schematic diagram of the CB096–5′CGG/3′GGC complex summarizing the noncovalent interactions that stabilize the small molecule-RNA complex with colors as indicated in panel d.