Figure 3.
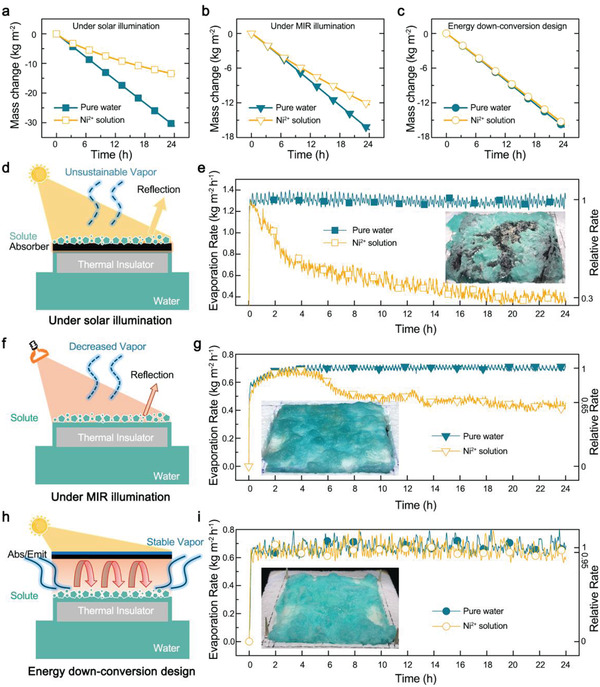
Evaporation performance during solute accumulation. a–c,e,g,i) Mass changes of a–c) water and e,g,i) corresponding water evaporation rates using a,e) a typical conventional iSTV under 1‐sun illumination, b,g) the iSTPV without the absorber/emitter structure under MIR illumination, and c,i) the iSTPV under 1‐sun illumination, that is the energy downconversion design. Insets in (e), (g) , and (i), photos of the paper surface after 24 h of continuous illumination. d) Schematic shows the accumulated solutes reflect sunlight strongly, resulting in unsustainable vapor generation in conventional iSTV. f) Schematic illustrating the low reflection of solutes lead to decreased while sustainable vapor generation under direct MIR illumination where water acts as its own absorber. h) Schematic illustrating the working principle of iSTPV as an efficient and stable solar evaporator during solute accumulation.
