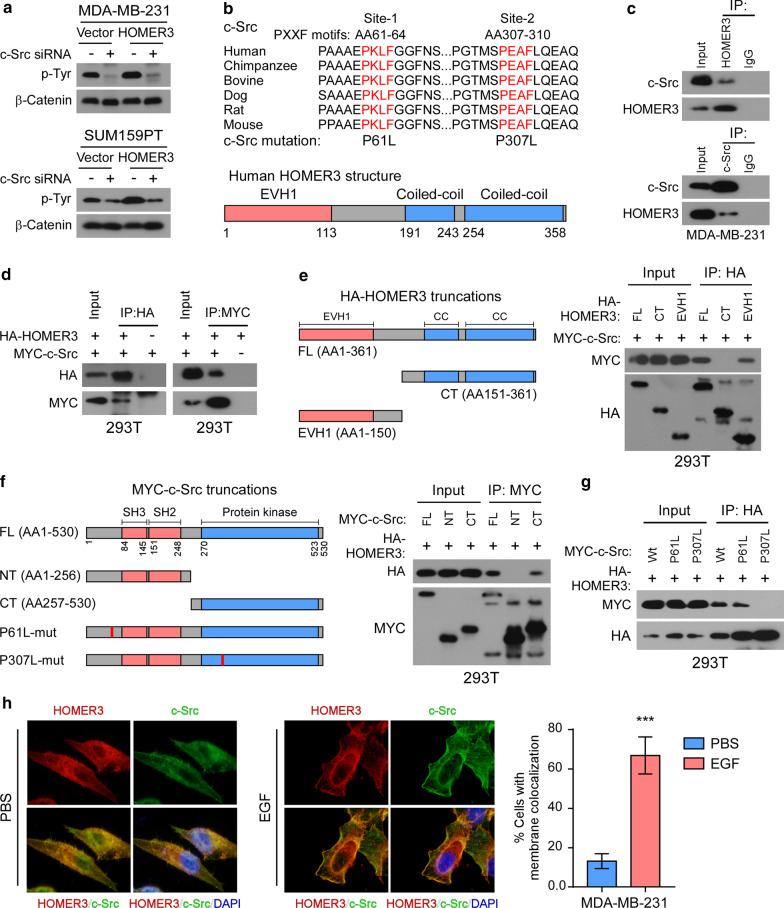
Fig. 3.
HOMER3 interacts with tyrosine-protein kinase c-Src. a Tyr phosphorylation levels of β-Catenin were examined in control and HOMER3-overexpressing MDA-MB-231 and SUM159PT cells with or without c-Src knockdown. b Schematic illustration of two conserved PxxF (x, any amino acid) motifs in c-Src protein that might be recognized by the EVH1 domain of HOMER3. c Immunoprecipitation (IP) assays determined the interaction between endogenous HOMER3 and c-Src in MDA-MB-231 cells. d IP assays were performed in 293 T cells transfected with HA-HOMER3 and MYC-c-Src constructs. e Left panel: Schematic illustration of HOMER3 truncated constructs. Right panel: The 293 T cells were transfected with indicated HA-tagged HOMER3 truncations and MYC-c-Src, followed by IP assays with HA-beads to examine their interaction with c-Src. f Left panel: Sketch of MYC-c-Src truncations. Right panel: The 293 T cells were transfected with indicated MYC-c-Src truncations and HA-HOMER3, followed by IP assays with MYC-beads to examine their interaction with HOMER3. g IP assays examined the interactions between HOMER3 and wild-type (wt) or mutant (P61L and P307L) c-Src proteins. h MDA-MB-231 cells were first stimulated with EGF for a short time, and then fluorescence immunostaining of HOMER3 and c-Src was performed to examine their colonization. Statistical analysis indicated the percentage of cells that showed membrane colonization of c-Src and HOMER3. ***P < 0.001