Fig. 1.
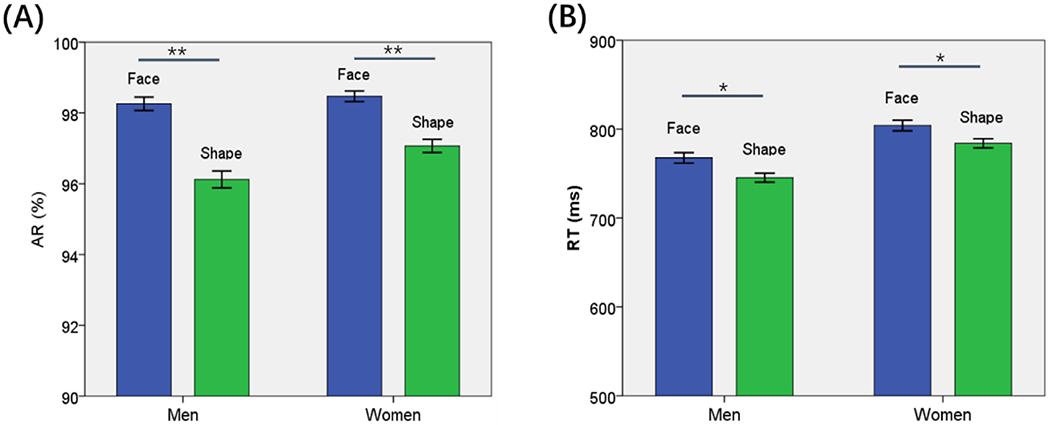
Behavioral results (mean ± SE) showed the (A) accuracy rate (AR) and (B) reaction time (RT) for face and shape stimuli each in men and women. AR was significantly higher for face than shape stimulus in both men and women but the difference was larger for men. Face trials showed slower RT than shape trials in both men and women. Women showed slower RT than men in both face and shape trials. **p < 0.001, *p < 0.05.
