Figure 2: Economic Outcomes of Early Infant Diagnosis Testing Platforms.
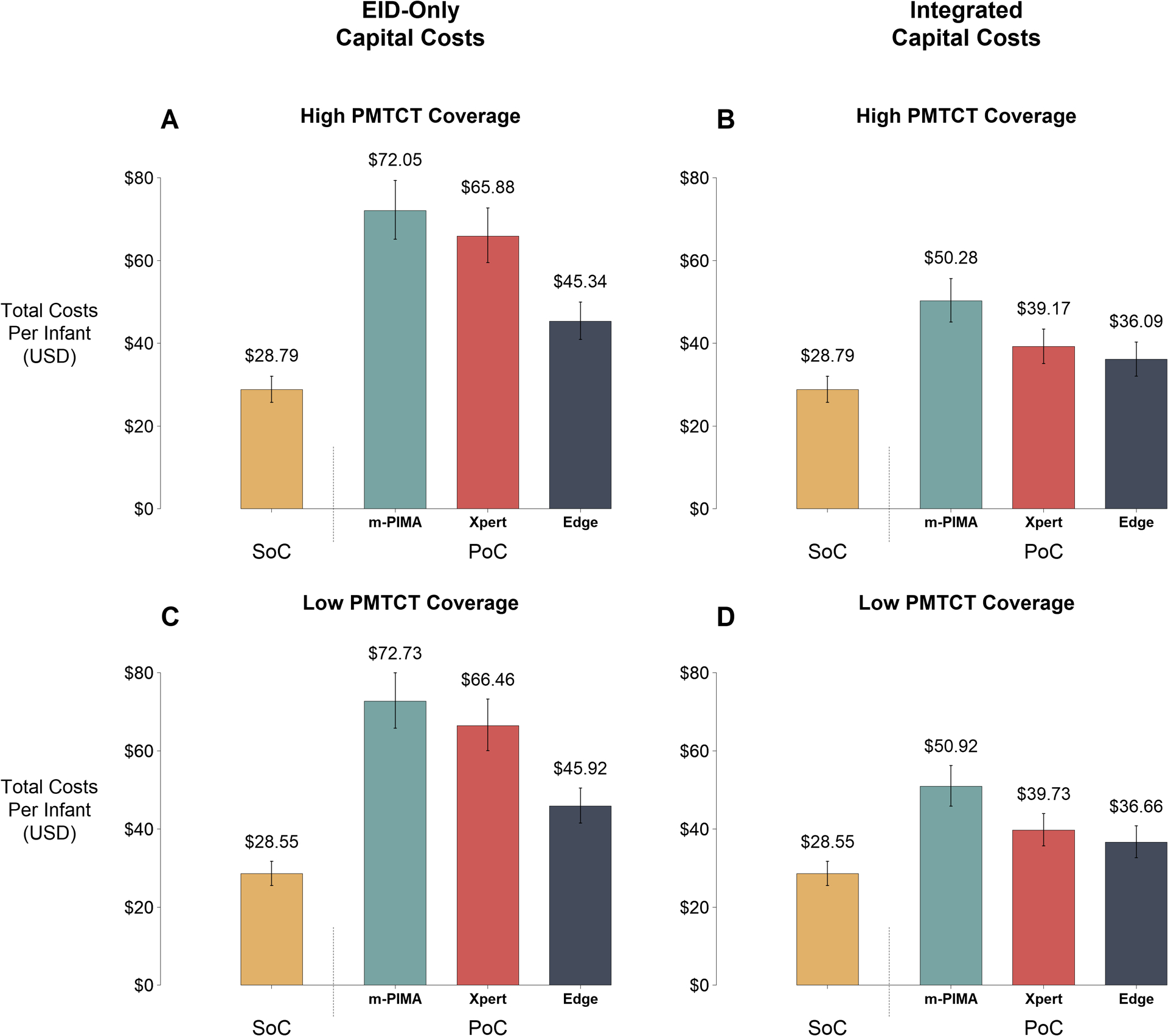
Total (capital and recurrent) programmatic costs per infant evaluated are plotted for the SoC and each PoC platform (m-PIMA, GeneXpert IV [Xpert], and GeneXpert Edge [Edge]). Data labels represent median costs per infant. Error bars represent 95% uncertainty ranges. Panels A and B represent a setting of high coverage of prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) programs (median: 93% coverage), while Panels C and D represent a setting of low PMTCT coverage (median: 48% coverage). Left panels (A and C) illustrate scenarios where all capital costs are borne by the early infant diagnosis (EID) testing program, while right panels (B and D) illustrate scenarios where capital costs are integrated across EID, HIV viral load, and tuberculosis testing programs according to instrument utilization proportions. All costs are expressed in 2018 USD.
