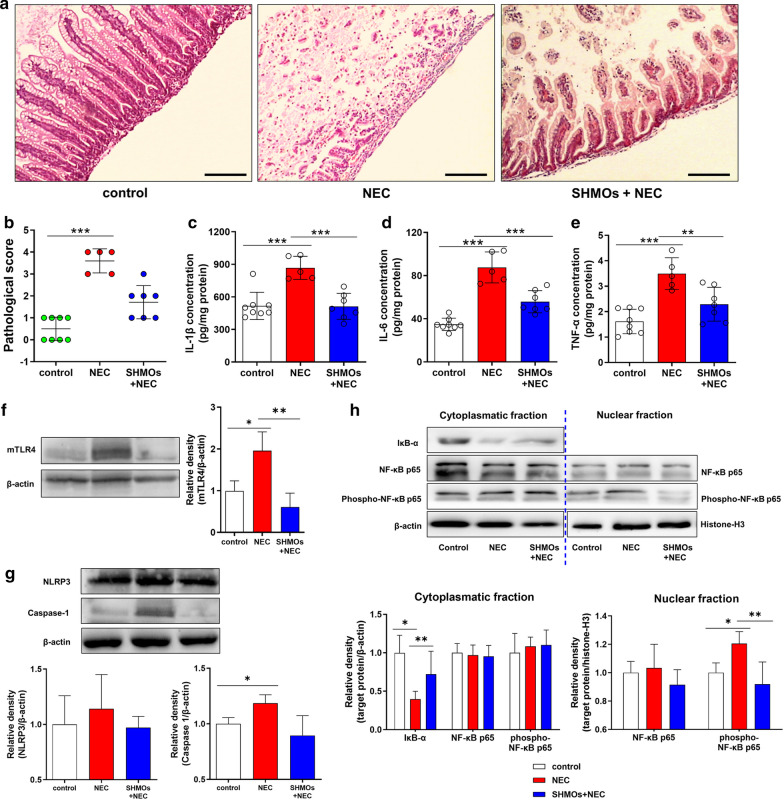
Fig. 2.
SHMOs prevented pathological damage and TLR4 mediated inflammatory cytokines release in NEC rats. a Histomorphology (HE staining, 100×) and b pathological scores of rats. Three groups of rats: (1) control group, rats fed with formula; (2) NEC group, rats fed with formula without SHMOs and exposed to 10-min hypoxia (5%O2, 95% N2) and 10-min cold stress (4 °C) thrice per day; (3) SHMOs + NEC group, rats fed with formula containing SHMOs (1500 mg/L) and exposed to hypoxia/cold stress. After 72 h, ileum samples of all surviving rats (control group, n = 8; NEC group, n = 5; SHMOs + NEC group, n = 7) were collected and examined. Scale bar represents 200 µm. Ileum c IL-1β, d IL-6 and e TNF-α concentrations were determined. The expression of f membrane TLR4 (mTLR4), g NLRP3 and caspase-1, as well as h IκB-α, NF-κB p65, phosphor-NF-κB p65 and nuclear NF-κB p65, phosphor-NF-κB p65 in the ileum of rats. Data were presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis test (b) or one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (c–h)