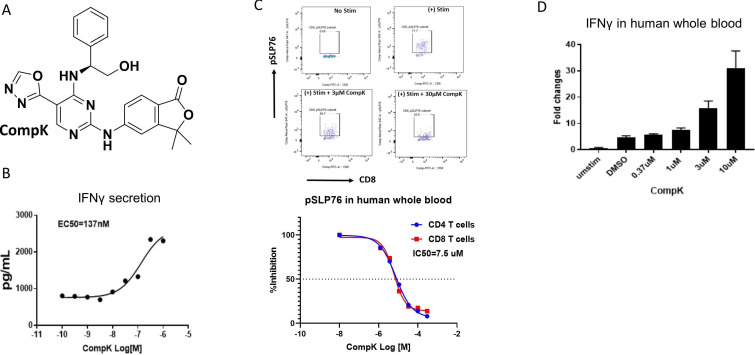
Figure 1.
Identification and characterization of selective HPK1 inhibitor, CompK. (A) Chemical structure of CompK. (B) Enhanced IFN-γ production in human CD8+ T cells by CompK. Cells were stimulated by anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for 48 hours in the presence of different concentrations of CompK followed by measurement of IFN-γ release. (C) Reduction of pSLP76 in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells by CompK in human whole blood. Heparinized fresh human whole blood was treated with CompK for 60 min followed by stimulation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for 15 min. Cells were stained and pSLP76 was measured by flow cytometry. (D) Increased production of IFN-γ by CompK treatment using human whole blood. Human whole blood was stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in the presence of different concentrations of CompK for 3 hours. Messenger RNA and complementary DNA were generated followed by quantitative PCR analysis. Studies were conducted with multiple donors; representative graphs are shown here. CompK, compound K; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; IFN-γ, interferon gamma.