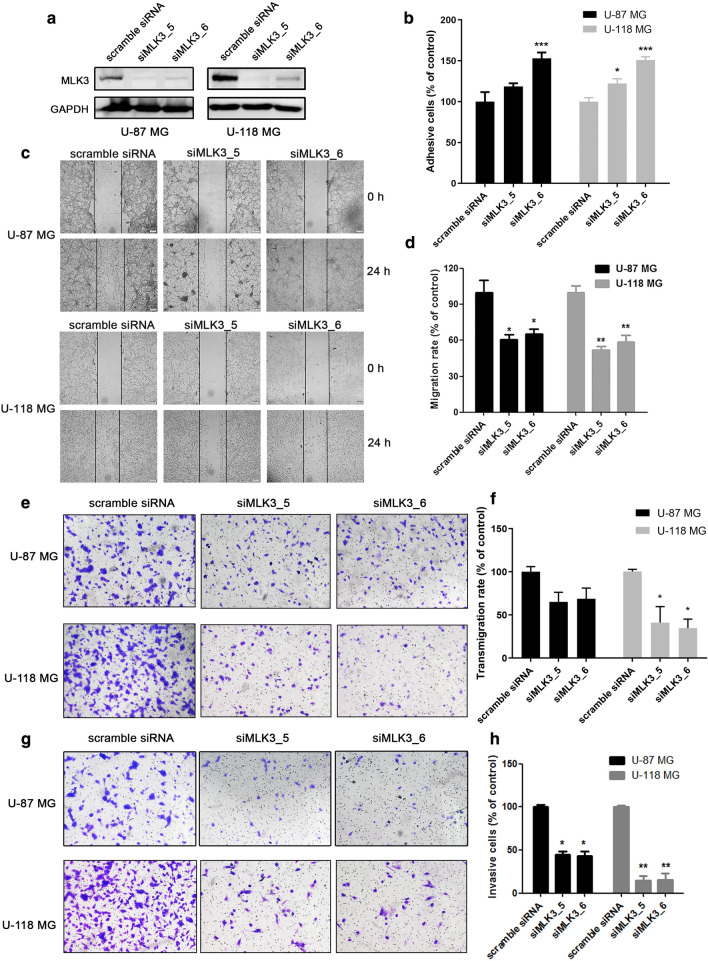
Fig. 2.
Knockdown of MLK3 markedly suppressed migration and invasion, but promoted attachment of glioblastoma cells. a siRNA-induced silencing of MLK3 (MAP3K11) gene in GBM cells U-87 MG and U-118 MG. Cells were incubated with siMLK3 duplexes (100 pmol) for 48 h. The AllStars Negative Control siRNA duplexes were denoted as “scramble siRNA” and used as a negative control. b Cell attachment assay showed that knockdown of MLK3 significantly increased adhesion of U-87 MG and U-118 MG cells to matrigel matrix. c, d Wound healing assay in U-87 MG and U-118 MG cells to evaluate the effect of MLK3 silencing on cell-to-cell migration. Cells were pretreated with 5 μg/mL of mitomycin C for 1 h. The lines indicate the edge of wound generated before drug treatment (0 h). Photographs were obtained at 40× magnification. e, f Boyden chamber migration assay in MLK3-silencing U-87 MG and U-118 MG cells. Representative photographs (100× magnification) showing the cells that had transmigrated through membrane to the lower surface. Cells from 5 representative fields were counted. (G-H) Boyden chamber invasion assay in MLK3-silencing U-87 MG and U-118 MG cells. Representative photographs (100× magnification) showing the invasive cells that had passed through matrigel to the lower surface of the membrane. Invaded cells from 5 representative fields were counted. n = 3; p values were determined by One-way ANOVA and Post Hoc multiple comparison Tukey HSD test. *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001