Table 1. Repurposing antivirals with potential ability to inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 replication via targeting the viral structural and nonstructural proteins.
| Existing antivirals | Chemical structure | Primary use | Potential efficacy on other viruses | Mechanism of action | Study (year) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Griffithsin |
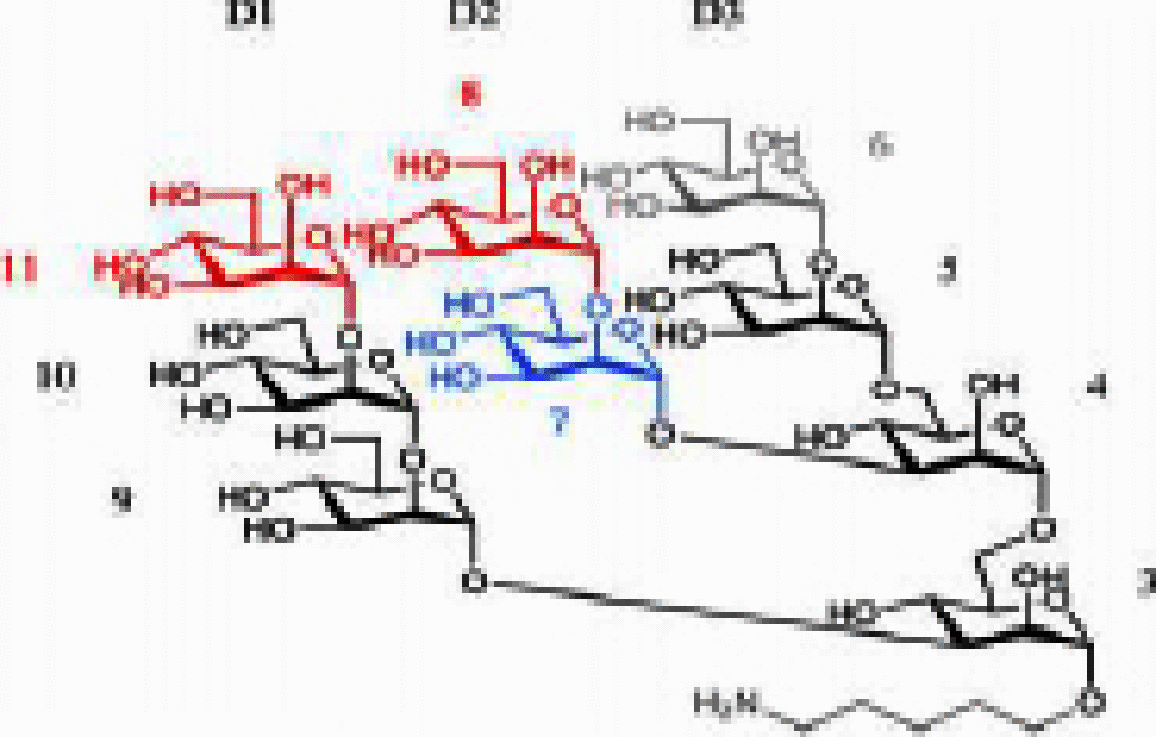 PubChem SID: 163672929 |
An alga-derived lectin against HIV | Broad-spectrum antiviral activity against HIV, SARS and MERS | Viral entry inhibition by attachment to the virus surface glycoproteins such as HIV gp120 and SARS-CoV-2 S protein | Lee et al. (2019) Fischer et al. (2019) Ziółkowska et al. (2006) Millet et al. (2016) |
[22–25] |
| Nafamostat |
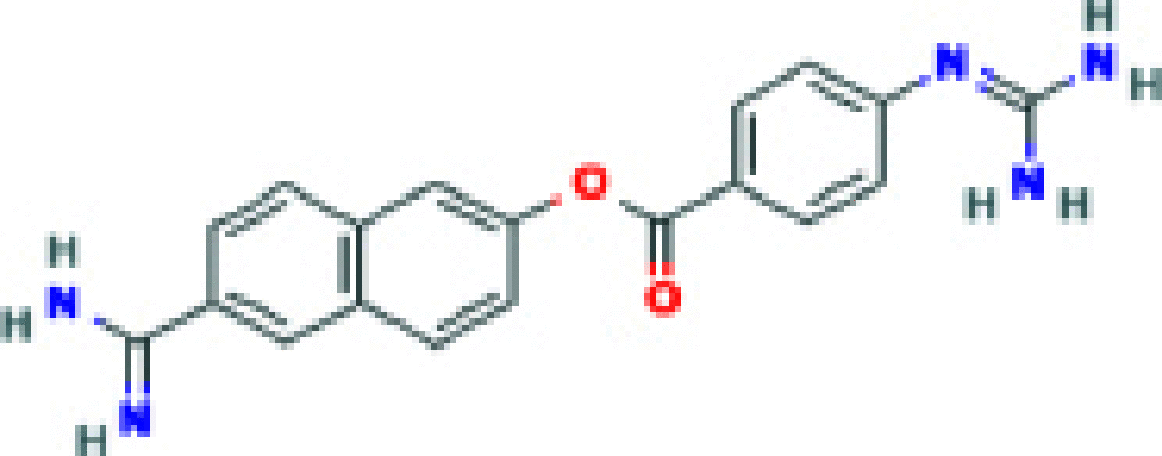 PubChem CID: 4413 |
A drug for acute pancreatitis | Inhibition the MERS and SARS-CoV-2 life cycle | Inhibiting the host cells protease (TMPRSS2) and virus membrane fusion | Yamamoto et al. (2016) | [28] |
| Disulfiram |
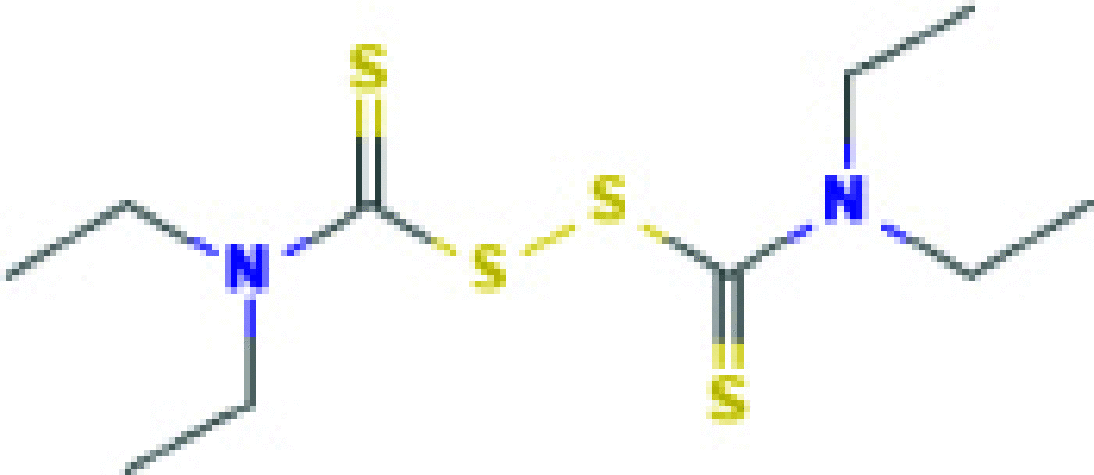 PubChem CID: 3117 |
A drug for chronic alcoholism | Potential treatment for HIV and inhibition ability for MERS and SARS-CoV-2 | Inhibit the viral polyprotein cleavage | Lin et al. (2018) Anand et al. (2003) Lee et al. (2016) |
[36–38] |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra) |
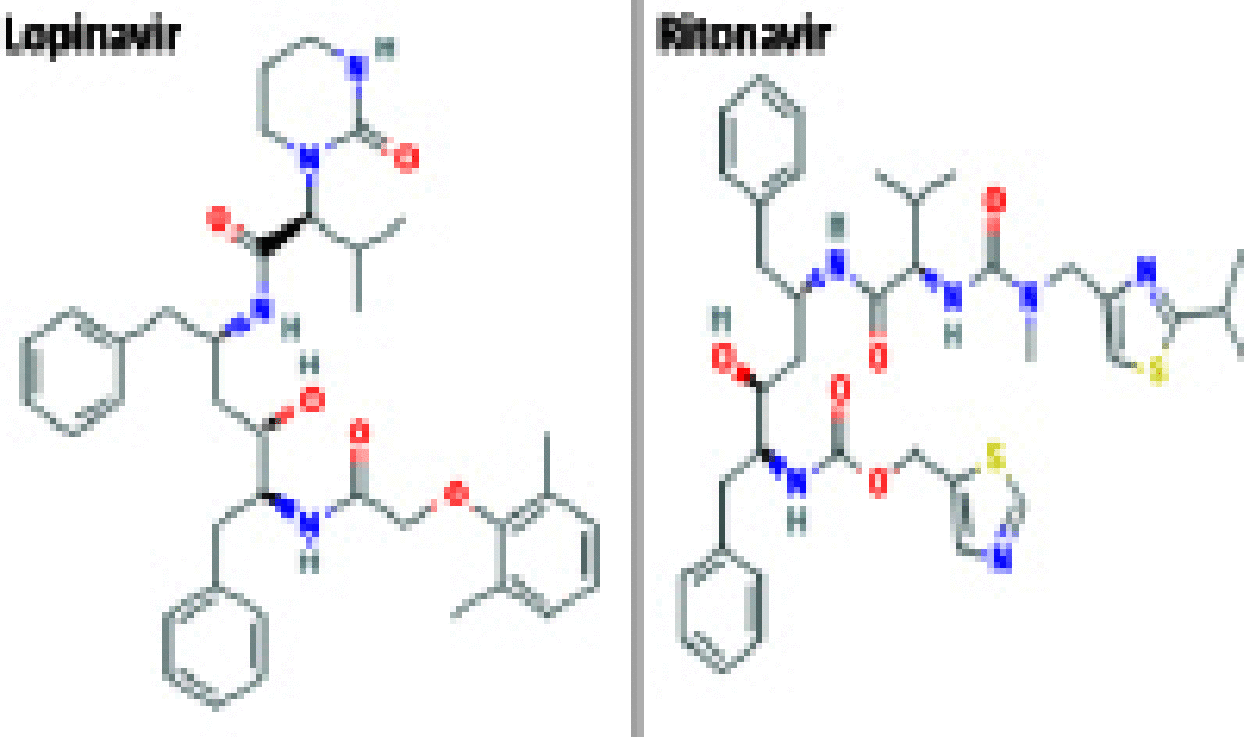 PubChem CID: 92727 PubChem CID: 392622 |
A drug to treat HIV | Inhibit the replication of the SARS, MERS and SARS-CoV-2 | Inhibiting the viral replication by high binding affinity to the viral protease | Chu et al. (2004) Yao et al. (2020) Cao et al. (2020) |
[46–48] |
| Nelfinavir |
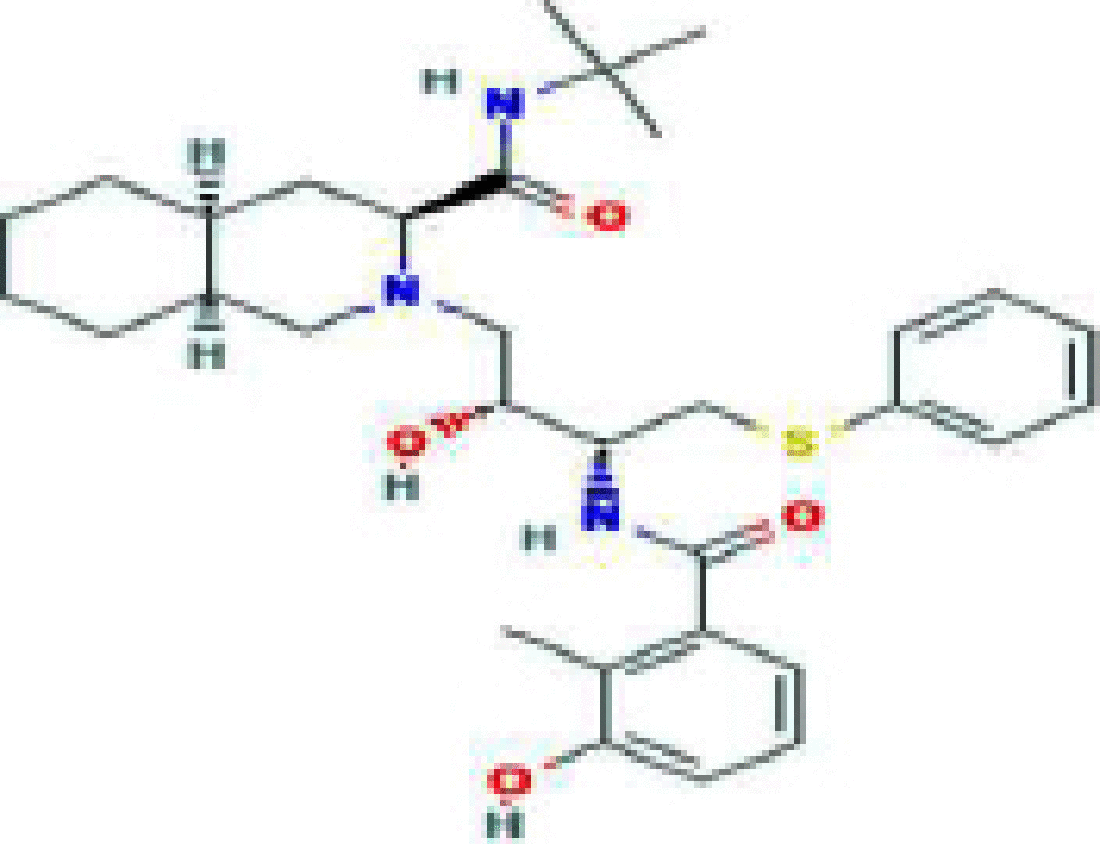 PubChem CID: 64143 |
Approved antiretroviral drug against HIV-1 | Inhibit the replication of the SARS and SARS-CoV-2 | Potential inhibitor against the viral protease such as 3CLpro | Xu et al. (2020) Yamamoto et al. (2004) Ohashi et al. (2020) |
[49,50,54] |
| Danoprevir |
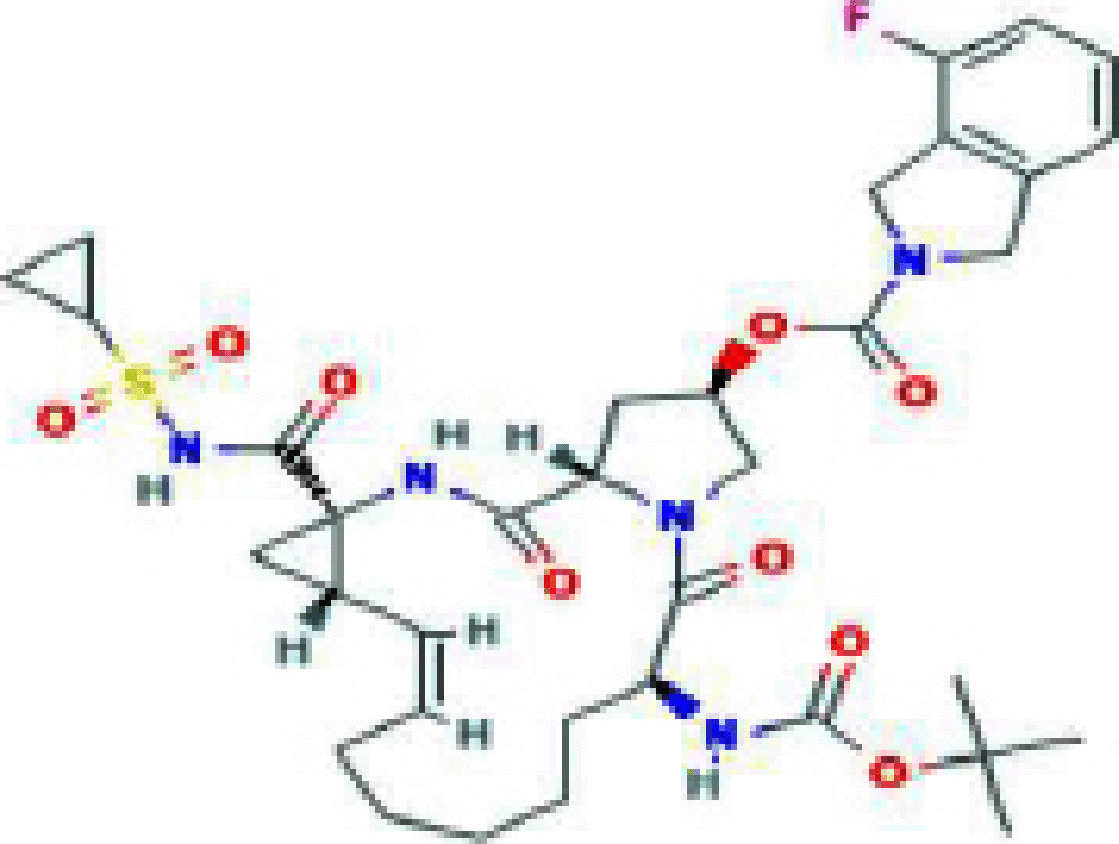 PubChem CID: 11285588 |
A drug for noncirrhotic genotype 1b HCV | Therapeutic potential against SARS-CoV-2 | Potential inhibitor against the viral protease such as 3CLpro | Chen et al. (2020) | [58] |
| Favipiravir (Avigan) |
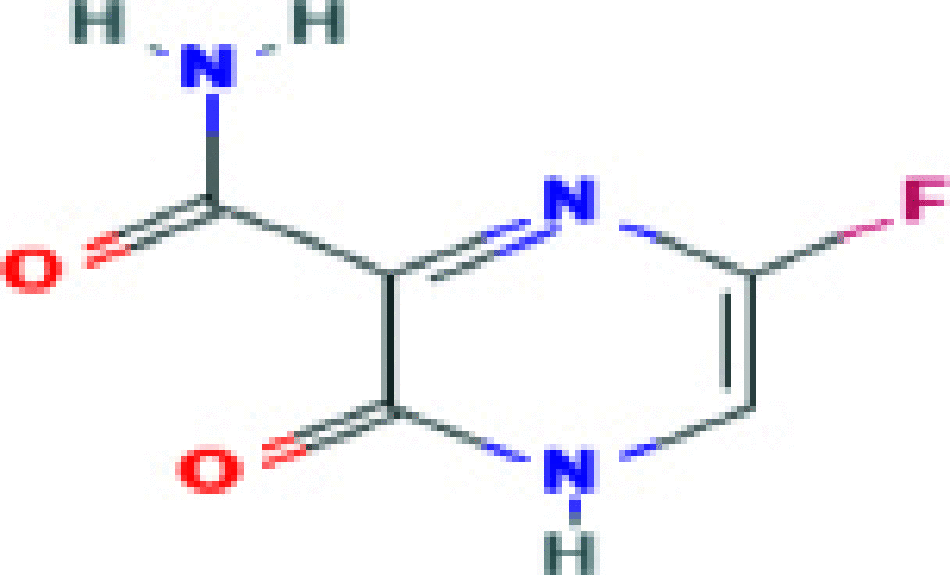 PubChem CID: 492405 |
A guanine analog flu drug | Activity against many RNA viruses such as influenza virus, yellow fever virus, enterovirus, SARS-CoV-2, … | Selectively inhibit the viral RdRp via tightly binding to the RdRp | Furuta et al. (2009) Furuta et al. (2013) Cai et al. (2020) |
[62,63,66] |
| Ribavirin |
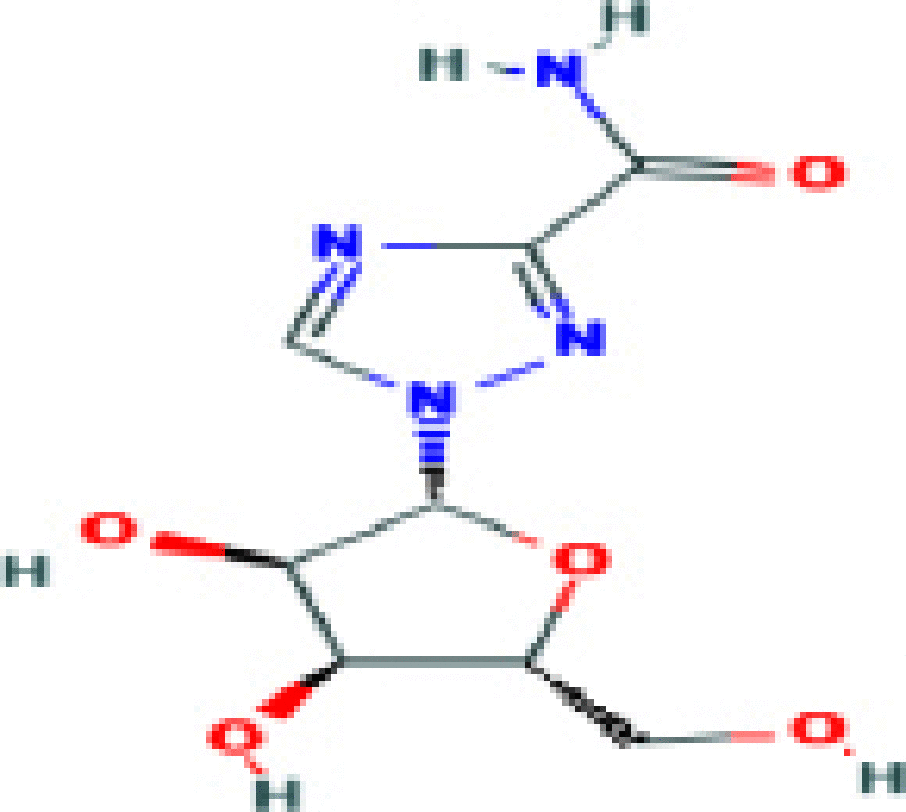 PubChem CID: 37542 |
An approved drug against HCV and RSV | Activity against of MERS and SARS-CoV-2 | Inhibition the viral RNA synthesis by viral mRNA capping termination via targeting the viral RdRp | Stockman et al. (2006) Arabi et al. (2020) |
[67,68] |
| Remdesivir |
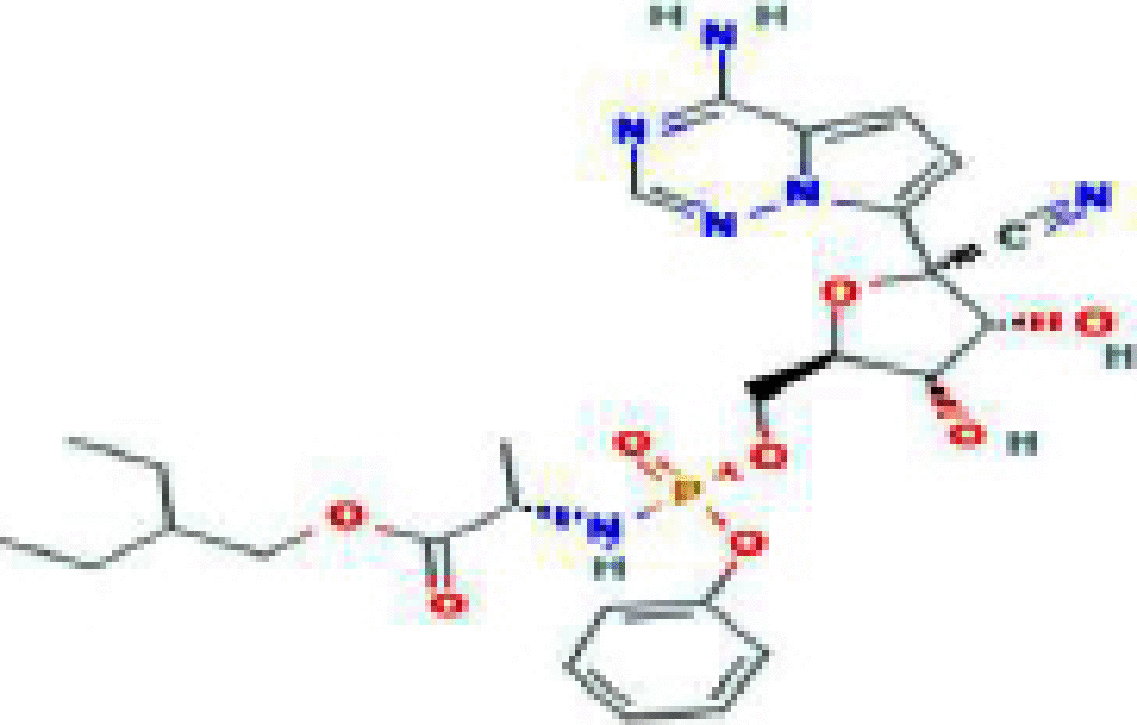 PubChem CID: 121304016 |
An adenosine analog developed in response to the Ebola virus | Broad-spectrum antiviral activity against a wide range of ssRNA viruses such as SARS, MERS, Marburg, RSV, SARS-CoV-2, etc. | Binds to the viral RdRp and acts as an RNA-chain terminator | Wang et al. (2020) Sheahan et al. (2017) Holshue et al. (2020) |
[65,69,71] |
| Galidesivir |
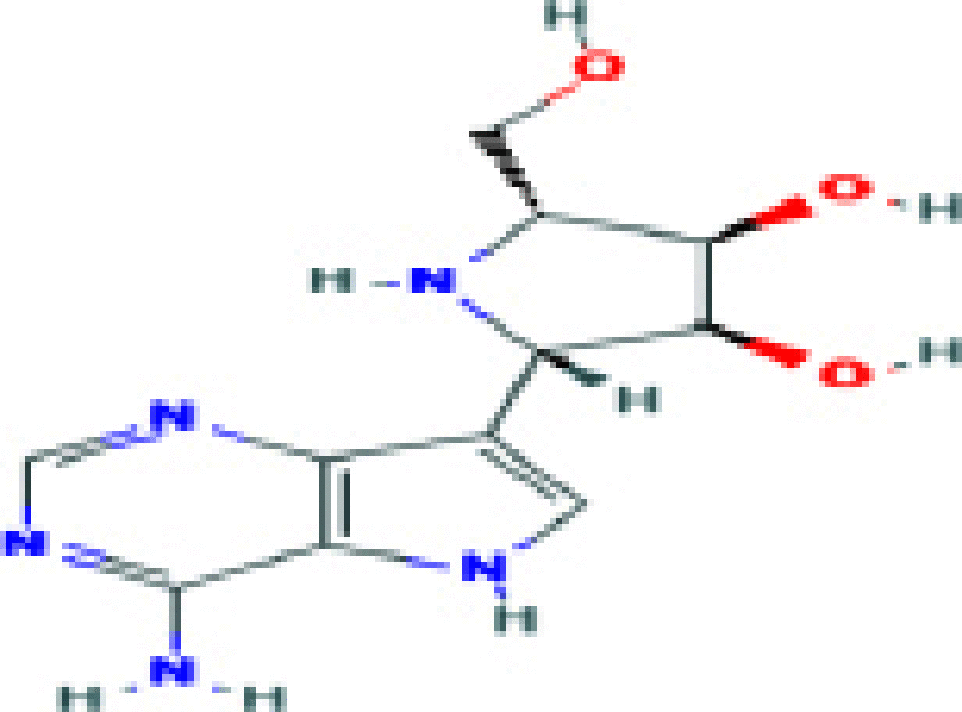 PubChem CID: 10445549 |
An adenosine analog developed in response to the HCV | Antiviral activity against a wide range of RNA viruses such as SARS-CoV, MER-CoV, Ebola and Marburg | Inhibition the viral RNA polymerase and premature termination of RNA transcription | Westover et al. (2018) | [74] |
The chemical structures of existing antivirals provided in Table 1 are derived from ‘PubChem’ database [75]. PubChem CIDs and SID are available in Table 1.
CID: PubChem’s compound identifier; Flu: Influenza; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; RdRp: RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; RSV: Respiratory syncytial virus; SID: PubChem’s substance identifier; TMPRSS2: Transmembrane protease serine 2.
