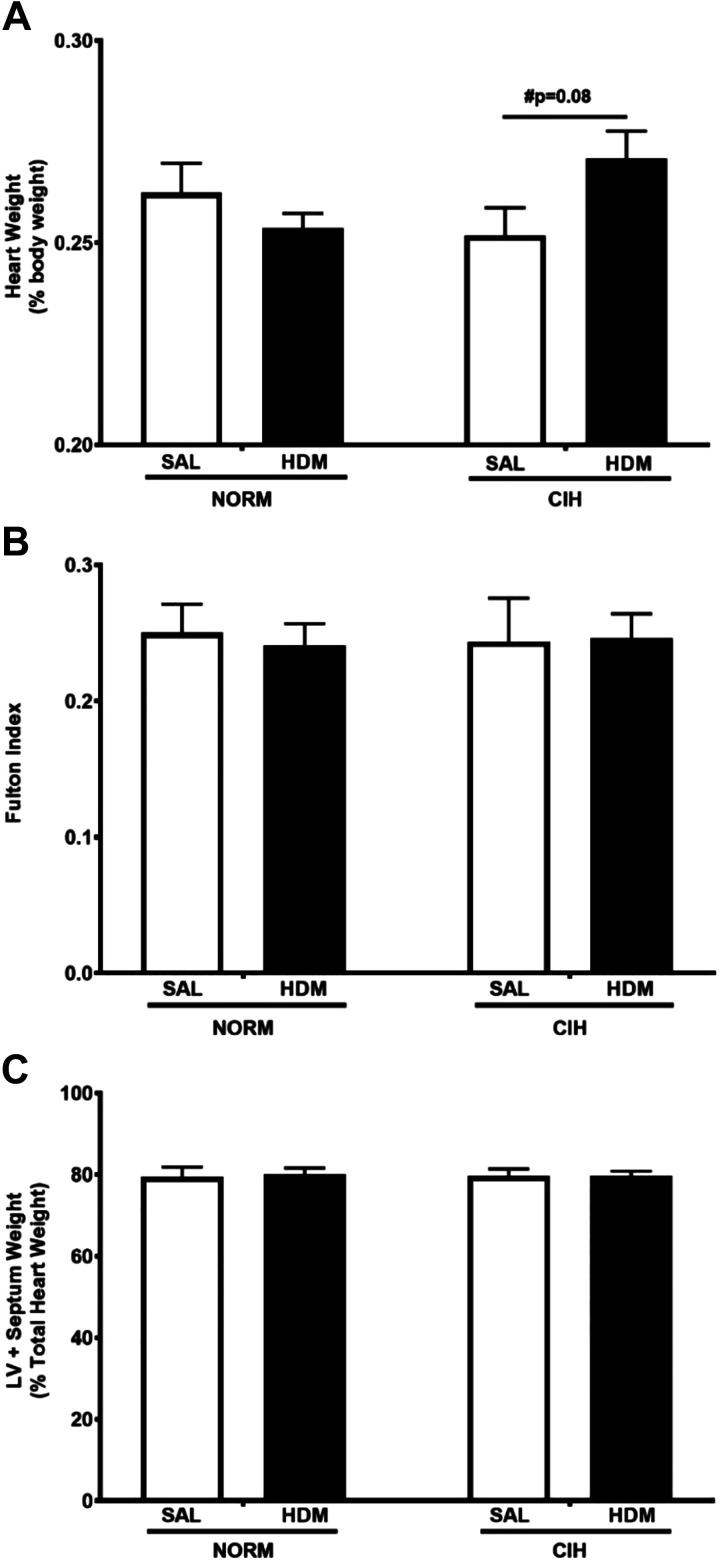
Fig. 3.
Chronic house dust mite-induced airway inflammation tended to increase heart weight in chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH)-exposed animals. No statistically significant differences among any treatment groups were noted in Fulton index or in left ventricle (LV) plus septum weight. A: heart weight, expressed as %total body weight. N = 10 animals/group. P values: Holm-Sidak post hoc tests after 2-way ANOVA. #Trend (0.05 ≤ P ≤ 0.1). B: Fulton index (ratio of weight of right ventricle/weight of left ventricle plus septum). C: left ventricle plus septum weight (%total heart wt). SAL, saline; HDM, house dust mite; NORM, normoxia. Data are presented as means ± SE.