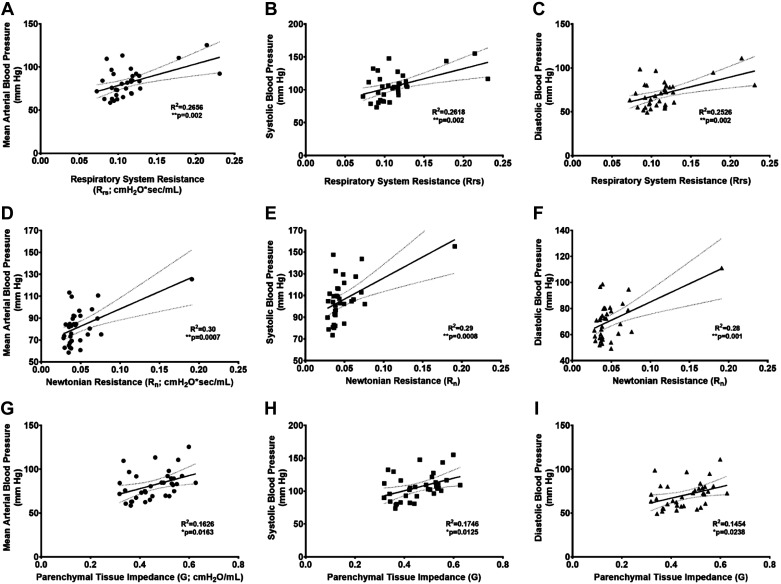
Fig. 5.
Worse distal airway obstruction induced by allergic airway inflammation was associated with higher systemic blood pressure. Increased total airway resistance (RRS) predicted higher mean (A), systolic (B), and diastolic (C) arterial blood pressure. A rise in central airway (Newtonian) resistance associated with elevated mean (D), systolic (E), and diastolic (F) arterial blood pressure. Parenchymal tissue impedance (G) was positively associated with mean (G), systolic (H), and diastolic (I) arterial blood pressure. Animals from all treatment groups are plotted. R2 and P values from linear regression analysis. *0.01 ≤ P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.