Fig. 4.
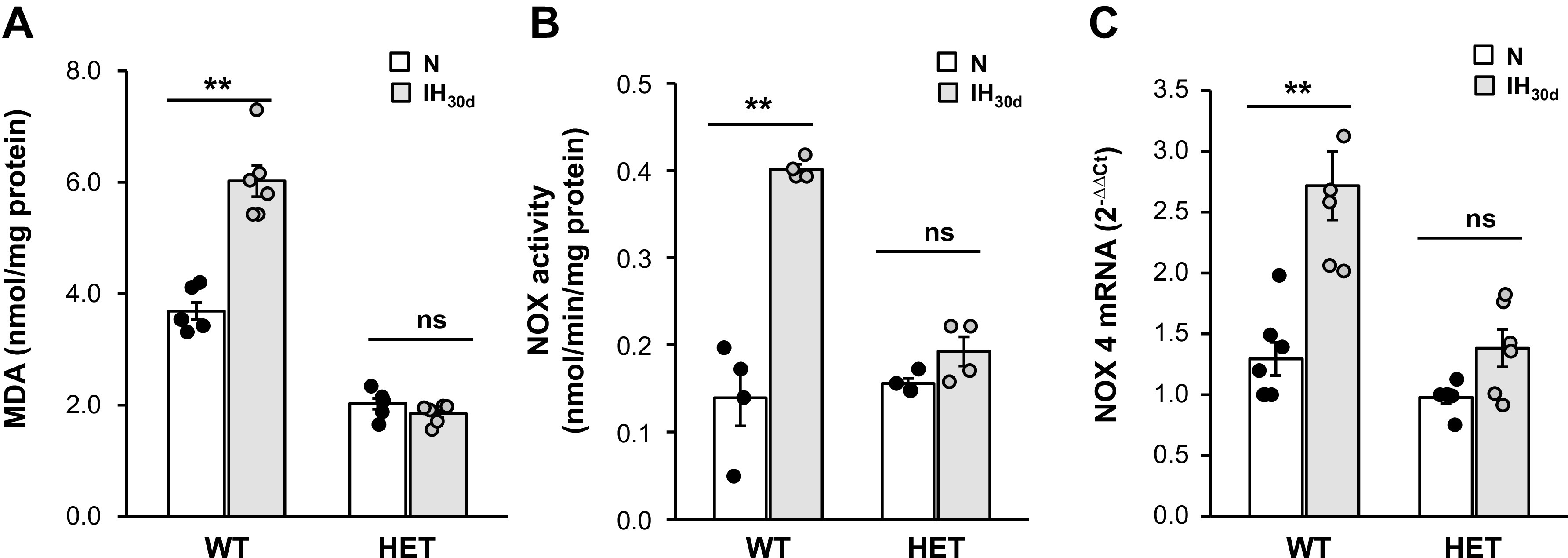
Intermittent hypoxia (IH) increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, NADPH oxidase (NOX) enzyme activity and NOX 4 mRNA in β-cells of wild-type (WT) but not in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) heterozygous (HET) mice. A: malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were determined in pancreatic islets as an index of ROS levels. B: NOX enzyme activity. C: NOX4 mRNA levels in islets from WT and HIF-1α HET mice exposed to room air (normoxia, N) or IH30d. Data from n = 6 animals as means ± SE. **P value <0.05; ns, not significant (P value > 0.05).
