Fig. 1.
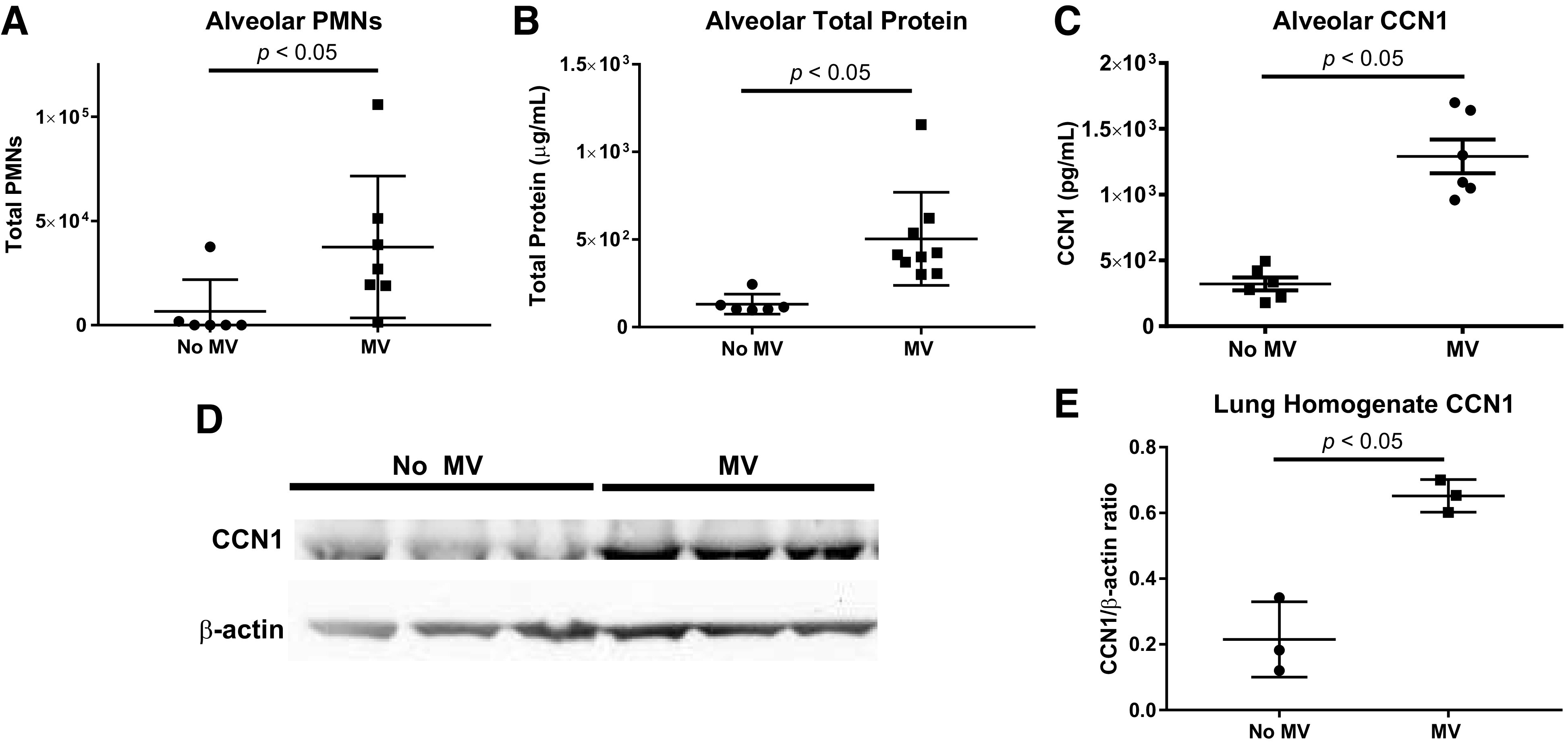
Soluble cellular communication network factor 1 (CCN1) bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) concentrations are increased in a ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) model. We measured BALF total neutrophils (PMNs), total protein, and CCN1 concentration in mice subjected to mechanical ventilation at a tidal volume of 20 mL/kg for 5 h (MV) vs. spontaneously breathing control mice (no MV). Shown are the individual values, mean, and standard deviation. All comparisons were made using t tests. A: BALF total PMNs were increased in mice subjected to MV vs. no MV. B: BALF total protein concentrations were increased in mice subjected to MV vs. no MV. C: BALF CCN1 concentrations were increased in mice subjected to MV vs. no MV. D: Western blot probed for CCN1 and β-actin using protein lysates from lung homogenates collected from MV vs. no MV mice. The entire Western blot gel is shown in Supplemental Fig. S1. E: quantification by densitometry revealed a significant increase in CCN1/β-actin ratio in MV vs. no MV mice.
