Fig. 5.
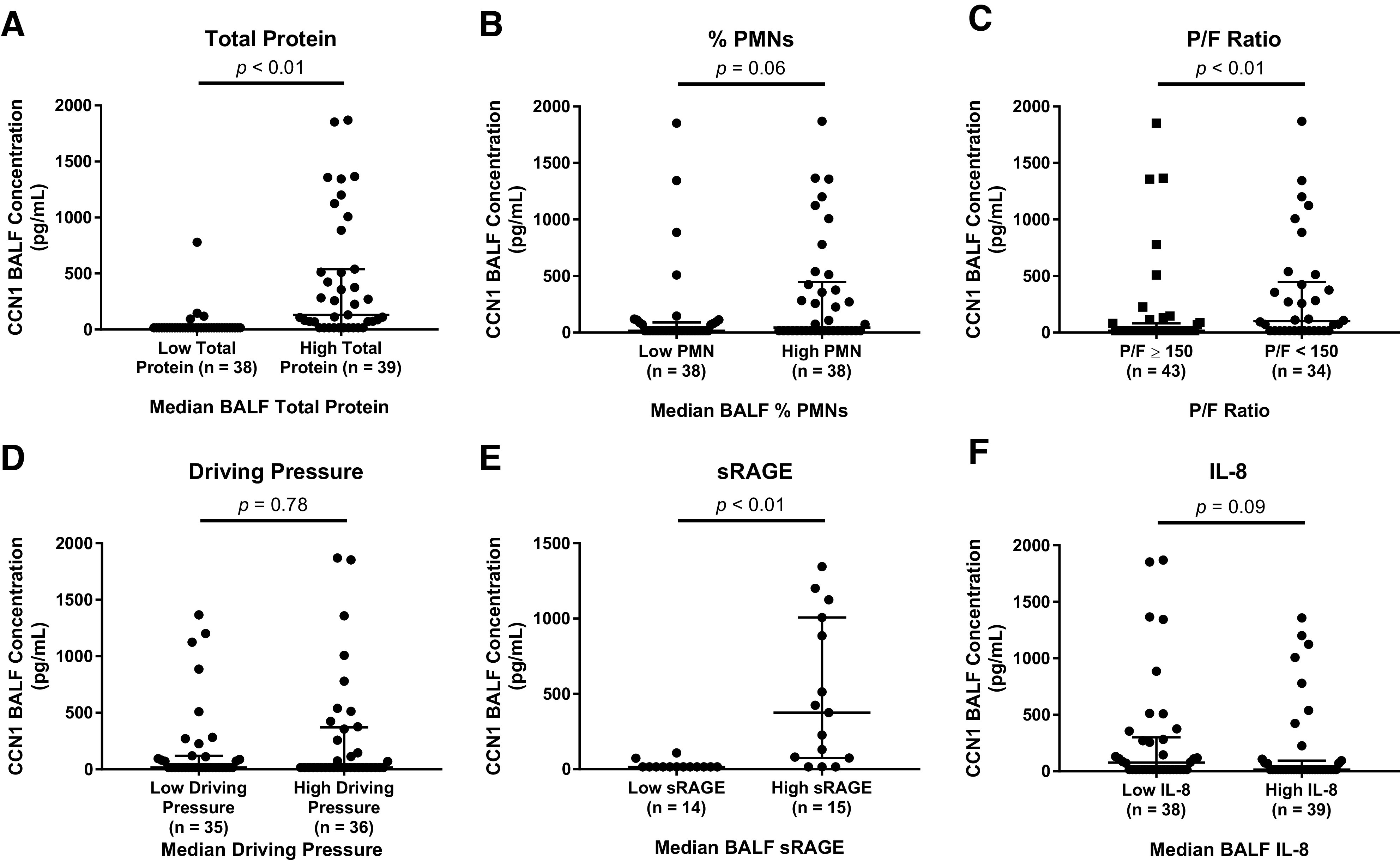
Cellular communication network factor 1 (CCN1) concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) are associated with total protein and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) severity. A: CCN1 concentrations were higher in subjects with high BALF total protein as compared with low BALF total protein. Subjects were divided by the median alveolar total protein concentration. B: CCN1 concentrations were higher in BALF from ARDS subjects with high %PMN (total number of alveolar neutrophils) vs. low %PMNs. Subjects were divided by the median %PMNs. C: BALF CCN1 concentrations were higher in ARDS subjects with a / (P/F) ratio of <150 vs. subjects with a P/F ratio of ≥150. D: BALF CCN1 concentrations were not different between subjects with low vs. high driving pressures. Subjects were stratified by the median driving pressure. E: BALF CCN1 concentrations were higher in ARDS subjects with high BALF sRAGE vs. low BALF sRAGE concentrations. Subjects were stratified by the median alveolar soluble form of receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) concentration. F: BALF CCN1 concentrations were not associated with BALF IL-8 concentrations in subjects with ARDS. Subjects were stratified by the median alveolar IL-8 concentration. We used an ELISA to measure CCN1 concentrations from BALF collected from subjects with ARDS. Shown are the individual values, median, and interquartile range. All comparisons were made using a Mann-Whitney test.
