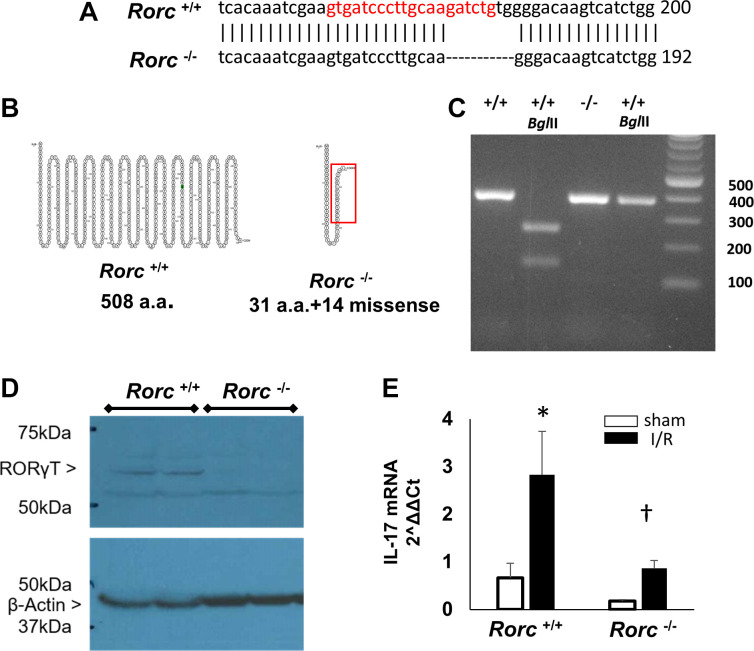
Fig. 2.
Generation and characterization of RAR-related orphan receptor C (Rorc) mutant rat. A: CRISPR/Cas9 was used to introduce a mutation in the rat Rorc gene of LEW/NCrl rat embryos by targeting the region shown in red of sequence XM_032897831.1. Gene sequencing identified an 8-bp deletion at nt 177–184. The resultant rat is referred to as LEW-Rorcem3Mcwi or hereafter in this report as Rorc −/−. B: the sequence predicted a full-length protein of 508 amino acids in Rorc+/+ rats, while the sequence in Rorc−/− rats predicted a missense mutation after amino acid 31, leading to premature truncation. The highlighted red box illustrates the area of missense relative to wild-type protein. C: genotyping of rats following PCR amplification and BglII digestion generated fragments in Rorc+/+ that are absent in Rorc −/−. D: Western blot using anti-RAR-related orphan receptor-γ (RORγT) identified a 55–60-kDa protein in the thymus from Rorc+/+ rats, which is not present in Rorc−/− rats. E: IL-17 mRNA expression in isolated CD4+ cells from the kidney following in vitro stimulation with elevated extracellular Na+ (170 mM) and ANG II (10−7 M). CD4+ cells were isolated from the kidney 7 days following ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury or sham from either Rorc+/+ or Rorc−/− rats. Data are normalized means ± SE of IL-17 mRNA, N = 3 rats per group, *P < 0.05 vs. sham, †P < 0.05 Rorc−/− vs. Rorc+/+ by one-way ANOVA and the Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc test.