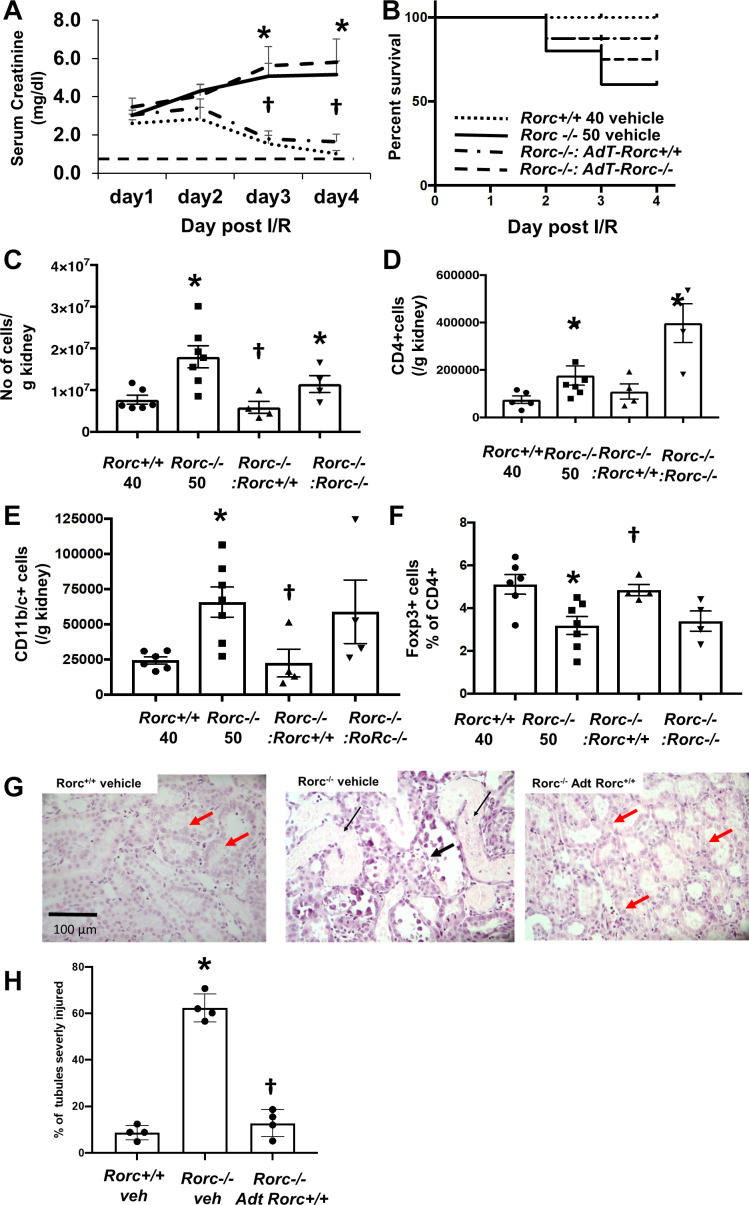
Fig. 5.
Rescue of RAR-related orphan receptor C (Rorc)−/− rats following bilateral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) by adoptive transfer of Rorc+/+ splenocytes. Rorc +/+ rats were subjected to 40 min of bilateral I/R and Rorc−/− rats were subjected to 50 min bilateral renal I/R. At the time of reperfusion, rats were provided with vehicle or adoptive transfer (AdT) of 1 × 106 splenocytes from either Rorc+/+ or Rorc−/− by intraperitoneal injection. A: daily serum creatinine values are shown for up to 4 days following I/R. B: Kaplan–Meier curve showing percent survival of rats following I/R injury and the effect of adoptive transfer. C–F: quantitative analysis of infiltrating cells 4 days following recovery from I/R injury expressed as positive cells per g kidney. Shown are total CD45+ cells (C), CD4+ cells (D), CD11/b/c+ (E), and % T-regulatory cells (F). G: representative renal histology 4 days following renal I/R of Rorc+/+ or Rorc−/− with adoptive transfer as labeled. Note the presence of necrotic cellular debris (thin black arrow) and thinned epithelial layer (thick black arrow) in outer medulla of Rorc−/− rats (arrows), while evidence of tubular repair containing a thicker epithelium (red arrows) was evident in Rorc+/+ kidneys or Rorc−/− kidneys following Adt of splenocytes from Rorc+/+ rats. H: percentage of severely damaged tubules from renal outer medulla of kidneys shown in G) Magnification is shown. For A, C–F, and H, values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05 in Rorc+/+vs. Rorc−/−rats; †P < 0.05 Rorc+/+adoptive transfer vs. Rorc−/−adoptive transfer in Rorc−/−rats, by one-way ANOVA and the Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc test.