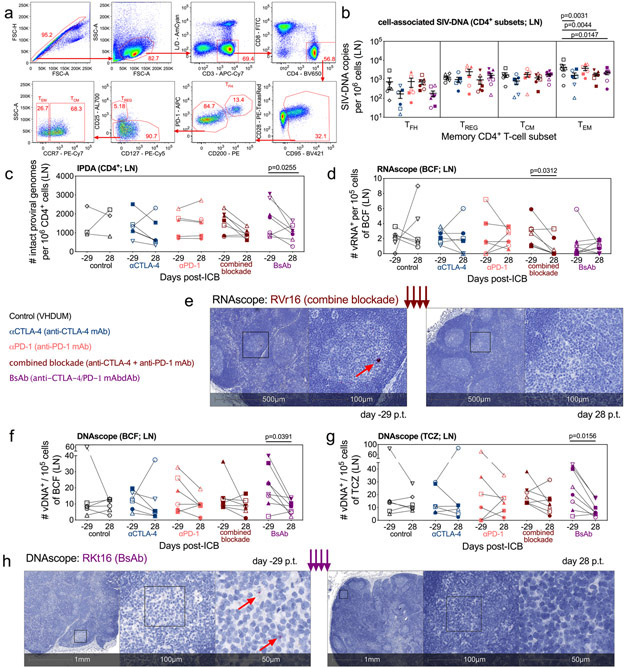
Figure 4. CTLA-4 and dual blockade, but not PD-1 blockade, reduces the total and intact SIV-DNA in LN.
In LN, memory subsets in CD4+ T-cells were sorted at d28 p.t., (a) as shown in this representative gating strategy (1 of 33 single-replicate runs; RTj16), and (b) the cell-associated SIV-DNA content was determined via 12 replicate reaction RT-qPCR. Within the memory CD4+ T-cells, the sorted populations are defined as follows: TFH, PD-1hiCD200hi; TREG, PD-1loCD200loCD127−CD25+; TCM, PD-1loCD200loCD25−CCR7+; and TEM, PD-1loCD200loCD25−CCR7−. (c) By 8 replicate reaction IPDA, the number of intact proviral genomes per 106 CD4+ cells were quantified in LN at pre-treatment baseline (d-29 p.t.) and following the fourth ICB (d28 p.t.): control (n=3), αCTLA-4 (n=6), αPD-1 (n=6), combined blockade (n=7), and BsAb (n=7). (d) By RNAscope, the number of vRNA+ cells per 105 cells were measured in the lymphoid B-cell follicle (BCF) and (e) a representative stain is shown for vRNA (red) in the LN BCF both pre- and post-treatment (combined blockade-treated RVr16; 1 of 33 unique samples quantified from up to two tissue sections). Distance scale is given below each panel with successive magnifications within the indicated area (black square) extending to the right. By DNAscope the number of vDNA+ cells per 105 cells were quantified in the lymphoid (f) BCF and (g) the T-cell zone (TCZ). (h) A representative stain (BsAb-treated RKt16; 1 of 33 unique samples quantified from up to two tissue sections) is shown for vDNA (red). For all analyses, except IPDA as indicated, annotations and population sizes are as follows: controls (n=6), black; αCTLA-4 (n=6), blue; αPD-1 (n=6), pink; combined blockade (n=7), red; and BsAb (n=8), purple. Individual RMs are indicated by shape with closed data points indicating viral reactivation in plasma. Averaged data are presented as the mean ± SEM, and were analyzed with a two-sided two-way ANOVA or mixed-effect model with (b) Dunnett’s correction relative to controls or (c) Bonferroni’s corrections for multiple comparisons relative to baseline, or (d,f,g) a Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test.